Professor Clare Rusbridge
About
Biography
Clare is Professor in Veterinary Neurology at University of Surrey and Senior Neurologist at Wear Referrals. Her experience with painful and distressing inherited and conformation related disease drives her research to improve diagnose, treatment and prevention of these conditions. She has spent over 25 years researching Chiari malformation, syringomyelia and neuropathic pain and has authored or co-authored over 160 scientific articles and book chapters including a textbook on human syringomyelia. She is a trustee for the Dog Breeding Reform Group and Patron of Cavalier Matters and Cure4DM charities. Her “hobby” is making content for her YouTube channel @clare-neurovet that, amongst other veterinary neurology content, has neuropathic pain and canine chiari-syringomyelia playlists.
Clare graduated from Glasgow University in 1991 and became a Diplomate of the European College of Veterinary Neurology in 1996 after a residency at the Royal Veterinary College. She became a RCVS Specialist in Veterinary Neurology in 1997 and was awarded a PhD from Utrecht University in 2007. She was honoured to receive the JA Wight Memorial award in 2011, made Fellow of the Royal College of Veterinary Surgeons (meritorious contribution to knowledge) in 2016, an RCVS Impact award in 2022, the Pet Plan Charitable Trust Scientific Award in 2023 and an APGAW unsung hero in 2023.
Areas of specialism
Affiliations and memberships
News
ResearchResearch interests
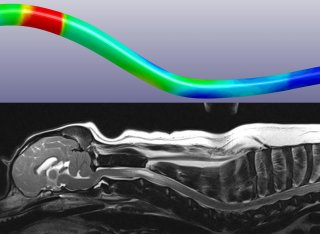
MRI conformational changes and dysmorphia associated with Chiari malformation
Clare provided the first description of this disease in the dog published in 2000 and came to realize quickly that this disorder was more than “cerebellar herniation” and was actually an extremely complex malformation of the skull and cervical vertebrae linked to brachycephalic head and facial characteristics. Understanding the way these conformation changes impact nervous tissue compliance and cerebrospinal fluid channels is key to understanding the pathogenesis of syringomyelia. Clare been primary, co-investigator or supervisor in over 20 projects on the morphometric changes associated with Chiari malformation and its association to syringomyelia. She has a close collaboration with Dr Kevin Wells (Reader in Medical Imaging) and Dr Serge Cirovic (Lecturer in Biomedical Engineering) both of whom are pivotal in helping to find engineering solutions to the clinical problems that she is trying to solve.
Genetics of Chiari malformation and syringomyelia
Since 2005, Clare Rusbridge and collaborator Dr Penny Knowler have had a partnership with Dr Kibar’s group of the University of Montreal with an aim of identifying genetic markers for canine CMSM and to translate the findings into genomic studies on humans. Prior to joining Surrey University they established a large database of DNA linked to MRI findings and over the last decade have refined phenotypical analysis of affected dogs and their diagnostic MRI in parallel with advances in statistical genetic analysis. Recently they identified strong candidate genes for CM in dogs and humans and SM in dogs which can be directly correlated to MRI morphometric traits and clinical findings of neuropathic pain. These findings have impact on understanding of the osseous changes in CM and why some patients are painful. In collaboration with the Medical Imaging Group at the University of Surrey they are now applying a machine learning approach to the significant MRI morphometric traits to establish a simple objective measure that could be applied to future genetic and other studies and develop a medical image analysis software that can be used to screen susceptible breeding dogs and be translated into human studies.
Progressive myoclonic epilepsy (Lafora’s disease)
Clare is the chief veterinary collaborator for an ongoing project on Lafora disease (a polyglucasan storage disease). After identifying this rare progressive myoclonic epilepsy in a canine patient in 2001, Clare established links with Dr. Berge Minassian of the Hospital for Sick Children, University of Toronto to study the mutation causing the disease. They established a nationwide program of DNA collection from affected dogs and their relatives to conduct a genome scan and characterization of the mutation. The successful outcome was the first description of a mutation causing canine epilepsy and the first example of a tandem repeat expansion outside of humans. This has led to better understanding of the disease in humans. In addition, a test for detection of affected and carrier dogs was established to enable a controlled breeding program in affected dog breeds. In the near future Clare hopes to establish a preventative treatment program that could be translated for human patients
Canine and feline epilepsy
Clare has been a member of the International Veterinary Epilepsy Task Force since its conception in 2013. This team’s mission statement is to suggest consensus statements and provide definitions for canine and feline epilepsy and to advance the field by doing collaborative research and exchanging ideas. Clare led the diagnostic imaging subgroup. So far the IVETF have produced seven consensus statements on the diagnosis, classification, treatment and genetics of canine epilepsy and one investigative study.
Head Space Project
The Head Space Project, led by Professor Clare Rusbridge at the University of Surrey, aims to revolutionize the detection and prevention of Chiari-like malformation (CM), syringomyelia (SM), and Brachycephalic Obstructive Airway Syndrome (BOAS) in dogs. Using advanced 3D imaging and artificial intelligence, the project developed a portable, low-cost system with five cameras to capture detailed 3D surface models of dogs’ heads in less than a second. This allows for real-time, non-invasive health assessments. The research has successfully linked specific head shape features to the likelihood of CM and SM, achieving up to 75% sensitivity and 70% specificity in disease prediction. This technology is being refined into a user-friendly app that could provide breeders and veterinarians with accessible tools to assess health risks and guide breeding decisions. Phase 2 of the project is focused on correlating internal skull conformation with external head shape and expanding the technology to address BOAS. By combining innovative imaging, AI, and collaborative efforts with organizations like Bliss Cavalier Rescue and the Cambridge BOAS Research Group, the Head Space Project addresses critical welfare issues in brachycephalic breeds, aiming to reduce inherited pathology and improve the health of future generations.
Research projects
Chiari Check is a free web-based diagnostic tool designed to help determine the likelihood of Chiari-like malformation-associated pain (CM-P) and syringomyelia (SM) in dogs. These painful and disabling neurological conditions are often difficult to diagnose during brief veterinary consultations and expensive to confirm by MRI.
Benefits: Cost-Effective Triage: Helps prioritise advanced diagnostics like MRI, which are expensive and not always accessible.
Support for Caregivers and their veterinary surgeons: Enables more informed decisions for managing potential cases of CM-P and SM especially for those caregivers unable to afford referral to a veterinary neurologist or for MRI
Research Contributions: Provides valuable clinical data for understanding these conditions, improving treatments, and assessing quality of life.
Scientific journals
Clare is a regular reviewer of scientific articles for BMC Veterinary, Veterinary Comparative Orthopedics and Traumatology, Journal of Small Animal Practice, Veterinary Record, Veterinary Radiology and Ultrasound, American Journal of Veterinary Research, Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine and occasionally other journals including Plos One and Nature.
Research interests
MRI conformational changes and dysmorphia associated with Chiari malformation
Clare provided the first description of this disease in the dog published in 2000 and came to realize quickly that this disorder was more than “cerebellar herniation” and was actually an extremely complex malformation of the skull and cervical vertebrae linked to brachycephalic head and facial characteristics. Understanding the way these conformation changes impact nervous tissue compliance and cerebrospinal fluid channels is key to understanding the pathogenesis of syringomyelia. Clare been primary, co-investigator or supervisor in over 20 projects on the morphometric changes associated with Chiari malformation and its association to syringomyelia. She has a close collaboration with Dr Kevin Wells (Reader in Medical Imaging) and Dr Serge Cirovic (Lecturer in Biomedical Engineering) both of whom are pivotal in helping to find engineering solutions to the clinical problems that she is trying to solve.
Genetics of Chiari malformation and syringomyelia
Since 2005, Clare Rusbridge and collaborator Dr Penny Knowler have had a partnership with Dr Kibar’s group of the University of Montreal with an aim of identifying genetic markers for canine CMSM and to translate the findings into genomic studies on humans. Prior to joining Surrey University they established a large database of DNA linked to MRI findings and over the last decade have refined phenotypical analysis of affected dogs and their diagnostic MRI in parallel with advances in statistical genetic analysis. Recently they identified strong candidate genes for CM in dogs and humans and SM in dogs which can be directly correlated to MRI morphometric traits and clinical findings of neuropathic pain. These findings have impact on understanding of the osseous changes in CM and why some patients are painful. In collaboration with the Medical Imaging Group at the University of Surrey they are now applying a machine learning approach to the significant MRI morphometric traits to establish a simple objective measure that could be applied to future genetic and other studies and develop a medical image analysis software that can be used to screen susceptible breeding dogs and be translated into human studies.
Progressive myoclonic epilepsy (Lafora’s disease)
Clare is the chief veterinary collaborator for an ongoing project on Lafora disease (a polyglucasan storage disease). After identifying this rare progressive myoclonic epilepsy in a canine patient in 2001, Clare established links with Dr. Berge Minassian of the Hospital for Sick Children, University of Toronto to study the mutation causing the disease. They established a nationwide program of DNA collection from affected dogs and their relatives to conduct a genome scan and characterization of the mutation. The successful outcome was the first description of a mutation causing canine epilepsy and the first example of a tandem repeat expansion outside of humans. This has led to better understanding of the disease in humans. In addition, a test for detection of affected and carrier dogs was established to enable a controlled breeding program in affected dog breeds. In the near future Clare hopes to establish a preventative treatment program that could be translated for human patients
Canine and feline epilepsy
Clare has been a member of the International Veterinary Epilepsy Task Force since its conception in 2013. This team’s mission statement is to suggest consensus statements and provide definitions for canine and feline epilepsy and to advance the field by doing collaborative research and exchanging ideas. Clare led the diagnostic imaging subgroup. So far the IVETF have produced seven consensus statements on the diagnosis, classification, treatment and genetics of canine epilepsy and one investigative study.
Head Space Project
The Head Space Project, led by Professor Clare Rusbridge at the University of Surrey, aims to revolutionize the detection and prevention of Chiari-like malformation (CM), syringomyelia (SM), and Brachycephalic Obstructive Airway Syndrome (BOAS) in dogs. Using advanced 3D imaging and artificial intelligence, the project developed a portable, low-cost system with five cameras to capture detailed 3D surface models of dogs’ heads in less than a second. This allows for real-time, non-invasive health assessments. The research has successfully linked specific head shape features to the likelihood of CM and SM, achieving up to 75% sensitivity and 70% specificity in disease prediction. This technology is being refined into a user-friendly app that could provide breeders and veterinarians with accessible tools to assess health risks and guide breeding decisions. Phase 2 of the project is focused on correlating internal skull conformation with external head shape and expanding the technology to address BOAS. By combining innovative imaging, AI, and collaborative efforts with organizations like Bliss Cavalier Rescue and the Cambridge BOAS Research Group, the Head Space Project addresses critical welfare issues in brachycephalic breeds, aiming to reduce inherited pathology and improve the health of future generations.
Research projects
Chiari Check is a free web-based diagnostic tool designed to help determine the likelihood of Chiari-like malformation-associated pain (CM-P) and syringomyelia (SM) in dogs. These painful and disabling neurological conditions are often difficult to diagnose during brief veterinary consultations and expensive to confirm by MRI.
Benefits: Cost-Effective Triage: Helps prioritise advanced diagnostics like MRI, which are expensive and not always accessible.
Support for Caregivers and their veterinary surgeons: Enables more informed decisions for managing potential cases of CM-P and SM especially for those caregivers unable to afford referral to a veterinary neurologist or for MRI
Research Contributions: Provides valuable clinical data for understanding these conditions, improving treatments, and assessing quality of life.
Scientific journals
Clare is a regular reviewer of scientific articles for BMC Veterinary, Veterinary Comparative Orthopedics and Traumatology, Journal of Small Animal Practice, Veterinary Record, Veterinary Radiology and Ultrasound, American Journal of Veterinary Research, Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine and occasionally other journals including Plos One and Nature.
Supervision
Postgraduate research supervision
PhD (Completed)
Susan Penelope Knowler, University of Surrey - Quantitative analysis of Magnetic resonance imaging in Canine Chiari-like malformation (Co Supervisor with Prof R. La Ragione)
Postgraduate research supervision
Masters of Research (Completed)
Fraye Watson - A Comparison of Brain Volume and Behavioural Changes in Dogs with Idiopathic Epilepsy (co-supervised with Prof H Volk, Royal Veterinary College)
Teaching
Professor Clare Rusbridge is an accomplished educator in veterinary neurology, recognized for her engaging and impactful teaching across various platforms. She contributes to undergraduate and postgraduate veterinary education at the University of Surrey, delivering comprehensive content on neurology, including clinical problem-solving, diagnostic techniques, and treatment planning for neurological disorders. She also contributes to the Veterinary General Practice PGCert to prepare vets for Royal College of Veterinary Surgeons examinations or re-entry into practice. In addition to formal education, Professor Rusbridge frequently lectures at professional conferences and events in the UK and internationally, such as the ISFM BSAVA, University of Copenhagen Masters Course, Central CPD, AVSPNI, StreetVet and Canine Arthritis Management. She has contributed to Podcasts and has her own YouTube Channel with educational contect. Through her teaching, she combines cutting-edge research with real-world application, inspiring veterinary professionals and advancing animal health and welfare.
Publications
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) plays a crucial role in maintaining brain homeostasis by facilitating the clearance of metabolic waste and regulating intracranial pressure. Dysregulation of CSF flow can lead to conditions like syringomy-elia, and hydrocephalus. This review details the anatomy of CSF flow, examining its contribution to waste clearance within the brain and spinal cord. The review integrates data from human, canine, and other mammalian studies, with a particular focus on brachycephalic dogs. Certain dog breeds exhibit a high prevalence of CSF-related conditions due to artificial selection for neotenous traits, making them valuable models for studying analogous human conditions, such as Chiari-like malformation and syringomyelia associated with craniosynostosis. This review discusses the anatomical features specific to some brachycephalic breeds and the impact of skull and cranial cervical conforma-tion on CSF flow patterns, providing insights into the pathophysiology and potential modelling approaches for these conditions.
Background: Although persistent fontanelles (PFs) are common in adult Chihuahuas, their association with cranial morphology remains unknown. Objectives: To identify whether cranial morphology is associated with PFs in Chihuahuas and if bodyweight is associated with cranial morphology in this breed. Animals: Fifty client-owned Chihuahuas. Methods: In this retrospective cross-sectional study using computed tomography images, we measured two different cranial base lengths (1 and 2), cranial length, height, and width, and two craniofacial angles. We calculated the ratios of cranial height to cranial base lengths 1 and 2, cranial height to length, cranial height to width, and cranial width to length (cranial index [CrI]). We evaluated if total PF area and number of cranial sutures affected by PFs were associated with craniometric measurements and their ratios and craniofacial angles. Additionally, we evaluated if the craniometric ratios were associated with bodyweight. Results: Total PF area was larger and number of cranial sutures affected by PFs higher in dogs with higher cranial height to cranial base length ratios 1 (estimate, [95% confidence interval], p: 2.295, [1.204-4.377], p = 0.01 and 1.720, [1.212-2.442], p = 0.002, respectively) and 2 (1.203, [1.069-1.354], p = 0.003 and 1.087, [1.011-1.169], p = 0.02, respectively) and CrI (1.225, [1.079-1.391], p = 0.002, and 1.134, [1.057-1.215], p < 0.001, respectively). Higher CrI was associated with lower bodyweight (-2.600, [-4.102 to -1.098], p = 0.001). Conclusion and Clinical Importance: Our results suggest that in Chihuahuas, lower bodyweight is associated with more extreme brachycephaly and extreme brachycephaly is associated with PFs.
Veterinary Ramblings - Exploring Genetic Disorders in Dogs 11th October 2024 https://veterinaryramblings.com/en_gb/episode/exploring-genetic-disorders-in-dogs-with-clare-rusbridge/ Discussed the challenges of diagnosing and managing Chiari like malformation and syringomyelia, the genetic and breeding factors involved, and the significant impact on canine health. The discussion touches on Professor Rusbridge’s efforts to develop better screening methods and public awareness, alongside her struggles against breeder resistance.The episode also explores broader topics like the influence of human preferences on dog breeding, veterinary pressures, and Professor Rusbridge’s personal insights into balancing a demanding career in veterinary medicine with her passion for practicing yoga.
Blackwell’s Five-Minute Veterinary Consult: Canine and Feline, 7th Edition provides up-to-date information on feline and canine disease in the familiar, popular, and trusted 5-Minute Veterinary Consult format. This reference puts all the necessary information regarding common diseases and conditions in dogs and cats at the reader’s fingertips. Covering 845 specific disorders, Blackwell’s Five-Minute Veterinary Consult is the most comprehensive and timely reference on canine and feline medicine available today.
Tremor is an involuntary, rhythmic, oscillatory movement of a body part produced by alternating contractions of reciprocally innervated muscles. Tremor is easy to see but more difficult to categorize and treat. It may be seen in isolation or in conjunction with other neurological conditions, for example, movement disorders such as paroxysmal dyskinesia
The policy document, "Dog Breeding Practices Must Change: Welfare Cost of Cuteness," highlights the urgent need to reform unethical dog breeding practices that prioritize aesthetics over animal welfare. Authored by Professor Clare Rusbridge, it underscores the widespread suffering caused by inbreeding and exaggerated physical traits, particularly in breeds like Cavalier King Charles Spaniels and other brachycephalic dogs. The report advocates for legislative changes, crossbreeding programs, and an overhaul of breed standards to prioritize health and genetic diversity. Drawing on research from the University of Surrey, it exposes how these practices contravene the Animal Welfare Act (2006) and contribute to serious health issues such as Chiari-like malformation and syringomyelia. The document calls for collaboration between policymakers, breeders, and veterinarians to address these challenges. Featured in The Guardian 2nd June 2024 (https://www.theguardian.com/lifeandstyle/article/2024/jun/02/dog-breeds-must-be-rebooted-to-halt-health-problems-says-expert-has-said), discussed on Radio 5 Live (June 3, 2024), and showcased in a Sky News interview (June 4, 2024), the report has sparked significant dialogue across social media and beyond, emphasizing its importance in shaping the future of dog breeding.
Zero Pain Philosophy – Shoe Size and the wrong shaped brain 19th July 2024 Episode Description Professor Clare Rusbridge is a global thought leader in the management of syringomyelia, Chiari malformation and phantom scratching. To assist vets in treatment of these conditions, Clare has recently updated and released her 2024 treatment algorithms. In this episode, Matt discusses the new algorithms with Clare, as well as ensuring we have our diagnosis correct and also looking to the future with these diseases.On Apple Podcasts: https://podcasts.apple.com/ie/podcast/the-dr-sam-collins-podcast/id1533811424?i=1000569553071On Spotify: https://podcasters.spotify.com/pod/.../Shoe-size-and-the-wrong-shaped-brain-e2m38ne
Abstract Background Myoclonus has been described in aging Cavalier King Charles Spaniels (CKCS), but the natural course of the disease and response to treatment have not been described. Objectives Report the clinical features and course of myoclonus in CKCS. Animals Twenty‐seven caregivers provided questionnaire responses at a median of 24 months after the onset of myoclonus in their CKCS. Fifteen caregivers completed a second follow‐up questionnaire at a median of 17 months after submission of the first questionnaire. Methods The caregivers of affected CKCS were invited to provide video footage for review. Owners of CKCS with videos demonstrating myoclonus then completed the online questionnaire for further evaluation. A second shortened questionnaire was sent to participants at least 6 months after completion of the first. Results Most CKCS displayed spontaneous myoclonus affecting predominantly the head (25/27). Overall, the majority had episodes that increased in frequency (20/27) and severity (17/27). Eighteen dogs had developed changes in behavior since the onset of myoclonus. These dogs were typically older and had experienced myoclonic episodes for longer than dogs without behavioral changes. Generalized epileptic seizures were reported in 4/27 dogs. Ten dogs received medical treatment. Eight were prescribed levetiracetam; all had an initial decrease in episode frequency, but a subsequent increase in both frequency and severity of episodes was common. Conclusions and Clinical Importance Myoclonus in CKCS tends to progress in frequency and severity regardless of treatment. Progressive behavioral changes suggestive of cognitive decline are common. These findings support the possibility of an underlying neurodegenerative process.
The terminology of Chiari malformation and syringomyelia is variable and at times controversial. Individual specialists can be quite dogmatic over which name or expression is correct. In this appendix the nomenclature and classification of syringomyelia and Chiari malformations is reviewed briefly and arguments for and against the various terms are presented. A more detailed historical review is given in Chap. 1.
A breed-specific polymyositis is frequently observed in the Hungarian Vizsla. Beneficial clinical response to immunosuppressive therapies has been demonstrated which points to an immune-mediated aetiology. Canine inflammatory myopathies share clinical and histological similarities with the human immune-mediated myopathies. As MHC class II associations have been reported in the human conditions we investigated whether an MHC class II association was present in the canine myopathy seen in this breed. 212 Hungarian Vizsla pedigree dogs were stratified both on disease status and degree of relatedness to an affected dog. This generated a group of 29 cases and 183 "graded" controls: 93 unaffected dogs with a first degree affected relative, 44 unaffected dogs with a second degree affected relative, and 46 unaffected dogs with no known affected relatives. Eleven DLA class II haplotypes were identified, of which, DLA-DRB1* 02001/DQA1*00401/DQB1*01303, was at significantly raised frequency in cases compared to controls (OR = 1.92, p = 0.032). When only control dogs with no family history of the disease were compared to cases, the association was further strengthened (OR = 4.08, p = 0.00011). Additionally, a single copy of the risk haplotype was sufficient to increase disease risk, with the risk substantially increasing for homozygotes. There was a trend of increasing frequency of this haplotype with degree of relatedness, indicating low disease penetrance. These findings support the hypothesis of an immune-mediated aetiology for this canine myopathy and give credibility to potentially using the Hungarian Vizsla as a genetic model for comparative studies with human myositis.
SEIZURES are the one of the most common presentations in the neurological feline patient and can be a daunting prospect for the veterinary clinician. The list of possible differential diagnoses is huge and demands a careful and systematic diagnostic approach. This article steers the practitioner through the work-up and provides guidance on the provision and monitoring of antiepileptic drug therapy in cats.
Previous research in Cavalier King Charles Spaniels (CKCS) has found that Chiari-like malformation and syringomyelia (CM/SM) are associated with a volume mismatch between the caudal cranial fossa (CCF) and the brain parenchyma contained within. The objectives of this study were to i) compare cerebellar volume in CKCS (a 'high risk' group which frequently develops CM/SM), small breed dogs (medium risk - occasionally develop CM/SM), and Labradors (low risk -CM/SM not reported); ii) evaluate a possible association between increased cerebellar volume and CM/SM in CKCS; iii) investigate the relationship between increased cerebellar volume and crowding of the cerebellum in the caudal part of the CCF (i. e. the region of the foramen magnum). Volumes of three-dimensional, magnetic resonance imaging derived models of the CCF and cerebellum were obtained from 75 CKCS, 44 small breed dogs, and 31 Labradors. As SM is thought to be a late onset disease process, two subgroups were formed for comparison: 18 CKCS younger than 2 years with SM (CM/SM group) and 13 CKCS older than 5 years without SM (CM group). Relative cerebellar volume was defined as the volume of the cerebellum divided by the total volume of brain parenchyma. Our results show that the CKCS has a relatively larger cerebellum than small breed dogs and Labradors and provide evidence that increased cerebellar volume in CKCS is associated with crowding of cerebellum in the caudal part of the CCF. In CKCS there is an association between increased cerebellar volume and SM. These findings have implications for the understanding of the pathological mechanisms of CM/SM, and support the hypothesis that it is a multifactorial disease process governed by increased cerebellar volume and failure of the CCF to reach a commensurate size.
Inherited diseases commonly emerge within pedigree dog populations, often due to use of repeatedly bred carrier sire(s) within a small gene pool. Accurate family records are usually available making linkage analysis possible. However, there are many factors that are intrinsically difficult about collecting DNA and collating pedigree information from a large canine population. The keys to a successful DNA collection program include (1) the need to establish and maintain support from the pedigree breed clubs and pet owners; (2) committed individual(s) who can devote the considerable amount of time and energy to coordinating sample collection and communicating with breeders and clubs; and (3) providing means by which genotypic and phenotypic information can be easily collected and stored. In this article we described the clinical characteristics of inherited occipital hypoplasia/syringomyelia (Chiari type I malformation) in the cavalier King Charles spaniel and our experiences in establishing a pedigree and DNA database to study the disease.
A 10-year-old neutered male Persian cat and a 4-year-old spayed female domestic shorthair (DSH) cat were evaluated for acute-onset severe lateralising tetraparesis and hemiplegia, respectively. Both cats also had left-sided Horner's syndrome. Neurological examination of the cats localised the lesion to cranial to C5 in the Persian and the left cervical intumescence (C6–T2) in the DSH. Physical examinations were otherwise generally unremarkable. Routine laboratory tests and spinal radiography were normal for the Persian cat and were not performed for the DSH cat. A cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) tap was attempted for the Persian cat but aborted because of gross blood contamination, and was not performed for the DSH cat. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the Persian cat revealed a lesion within the spinal parenchyma at segments C1 to C3 (slightly more left-sided) which was iso- to hypointense on T1-weighted scans and hyperintense on T2-weighted scans, and which enhanced slightly with gadolinium. MRI of the DSH cat revealed a lesion within the spinal parenchyma at segment C7 (predominantly left-sided) which was hypointense on T1-weighted scans and hyperintense on T2-weighted gradient echo scans. Contrast was not administered. The MRI findings in both cases were highly suggestive of acute spinal cord infarction, based upon comparison to human cases. Both cats made full neurological recoveries with supportive treatment only. This paper describes two cases of suspected acute spinal cord infarction in the cat, demonstrates the potential diagnostic value of MRI, and discusses the clinical syndrome of this condition with a brief review of published cases.
In the past veterinary interest in snails has been confined to their role in the transmission of disease; nowadays the trend to keep these animals in captivity--for food, for study, as 'companion animals'--means that the profession is increasingly likely to be consulted about their health, welfare or conservation. An understanding of the biology of snails is an important prerequisite to work with them. Land snails are hermaphrodite and have a complex reproductive system; other organs also show special adaptations. Management methods vary considerably and farmed snails can be maintained under extensive or intensive conditions. Methods for handling and transporting them are important considerations. There is little published information on the diseases and pathology of snails but suboptimum environment, poisons, nutritional deficiencies, predators and parasites are known to cause, or contribute, to their mortality.
A database of over 1300 cavalier King Charles spaniels spanning 20 generations was established by obtaining pedigree information from 45 dogs with syringomyelia secondary to occipital bone hypoplasia. These data were supplemented with published information from the breed club. The incidence of syringomyelia was very high in certain families and lines which had been extensively inbred. The affected dogs could be traced back to one bitch born in 1956 and the two offspring from her single lifter. Four key dogs representing four major breeding lines consistently occurred within the individual pedigrees. If a dog had more than five of its eight great-grandparents descended from these four lines there was a greater chance of it having syringomyelia. The data from this preliminary study suggest that occipital bone hypoplasia is hereditary in the cavalier King Charles spaniel and that its inheritance is more likely to be autosomal recessive because both dam and sire must be inbred descendants from certain lines. However, the inheritance is more likely to be of variable penetrance or oligogenic than simple.
Several neurological syndromes have been described in Cavalier King Charles spaniels and many of the conditions have similar clinical signs. The current knowledge of these syndromes is reviewed in this article, with the aim of enabling the general practitioner to formulate a differential diagnosis and plan for diagnostic tests and treatment. Specifically, the article discusses and contrasts the most common conditions seen, Including occipital hypoplasia/syringomyelia, episodic collapse, epilepsy and vestibular disorders.
In 2015, the International Veterinary Epilepsy Task Force (IVETF) published the "Consensus Proposal: Diagnostic Approach to Epilepsy in Dogs", proposing the basis for a standardized method of diagnostic procedures in patients suffering from seizures. The recommended modus operandi comprises two fundamental steps to clarify if the patient is truly suffering from epilepsy and to determine its underlying cause. The authors suggest a tier system of three confidence levels describing the reliability of the diagnosis "idiopathic epilepsy" The authors of the consensus proposal emphasize that these recommendations will evolve over time with advances in neuroimaging, electroencephalography, and molecular genetics of canine epilepsy. In this article, the contents of the consensus proposal are summarized in German language.
Practical relevance: Chronic pain is a significant welfare concern in cats, and neuropathic pain, which arises from aberrant processing of sensory signals within the nervous system, is a subcategory of this type of pain. To comprehend this condition and how multimodal pharmacotherapy plays a central role in alleviating discomfort, it is crucial to delve into the anatomy of nociception and pain perception. In addition, there is an intricate interplay between emotional health and chronic pain in cats, and understanding and addressing the emotional factors that contribute to pain perception, and vice versa, is essential for comprehensive care. Clinical approach: Neuropathic pain is suspected if there is abnormal sensation in the area of the distribution of pain, together with a positive response to trial treatment with drugs effective for neuropathic pain. Ideally, this clinical suspicion would be supported by confirmation of a lesion at this neurolocalisation using diagnostic modalities such as MRI and neuroelectrophysiology. Alternatively, there may be a history of known trauma at that site. A variety of therapies, including analgesic, anti-inflammatory and adjuvant drugs, and neuromodulation (eg, TENS or acupuncture), can be employed to address different facets of pain pathways. Aim: This review article, aimed at primary care/ general practitioners, focuses on the identification and management of neuropathic pain in cats. Three case vignettes are included and a structured treatment algorithm is presented to guide veterinarians in tailoring interventions. Evidence base: The review draws on current literature, where available, along with the author's extensive experience and research.
Epilepsy afflicts 1% of humans and 5% of dogs. We report a canine epilepsy mutation and evidence for the existence of repeat-expansion disease outside humans. A canid-specific unstable dodecamer repeat in the Epm2b ( Nhlrc1 ) gene recurrently expands, causing a fatal epilepsy and contributing to the high incidence of canine epilepsy. Tracing the repeat origins revealed two successive events, starting 50 million years ago, unique to canid evolution. A genetic test, presented here, will allow carrier and presymptomatic diagnosis and disease eradication. Clinicopathologic characterization establishes affected animals as a model for Lafora disease, the most severe teenage-onset human epilepsy.
Objective Abnormalities within the spinal arachnoid space are often treated surgically, but they can be challenging to detect with conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) sequences. 3D-CISS sequences are considered superior in evaluating structures surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) due to the high signal-to-noise ratio, high contrast-to-noise ratio and intrinsic insensitivity to motion with minimal signal loss due to CSF pulsations. Our objective was to describe findings and advantages in adding 3D-CISS sequences to routine MRI in patients affected by spinal arachnoid diverticula (SAD) or arachnoid adhesions. Material and Methods This article is a retrospective review of medical records of 19 dogs admitted at Fitzpatrick Referrals between 2013 and 2017 that were diagnosed with SAD and confirmed surgically. Inclusion criterions were the presence of clinical signs compatible with compressive myelopathy and an MRI diagnosis, which included the 3D-CISS sequence. Our database was searched for additional 19 dogs diagnosed with other spinal lesions other than SAD that had the same MR sequences. All MR images were anonymized and evaluated by two assessors. Conclusion and Clinical Relevance 3D-CISS sequence appears to improve confidence in diagnosing and surgical planning (Mann-Whitney U-test: p < 0.0005), delineating SAD from other changes associated with abnormal CSF hydrodynamics and providing more anatomical details than conventional MRI sequences. The clinical data in combination with imaging findings would limit over interpretation, when concurrent pathology within the arachnoid space is present.
Mixed model analysis of 384 Cavalier King Charles spaniels (CKCS), with a magnetic resonance imaging diagnosis for the presence or absence of a syrinx, in conjunction with the Kennel Club pedigree records of all dogs registered from the mid 1980s to September 2007, revealed a moderately high estimate of heritability, of syringomyelia (h(2) = 0.37 +/- 0.15 standard error) when analysed as a binary trait. Inspection of cases where the disease segregated within families pointed to genes at more than one locus influencing syringomyelia. The availability of estimated breeding values for Kennel Club registered CKCS is a significant step in being able to select against syringomyelia, particularly given the difficulty of ascertaining the disease phenotype. (C) 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Molluscs of the genus Partula are threatened with extinction; captive populations of some species have shown a marked and unexplained decline in numbers. Histopathological, electron microscopical and bacteriological studies were carried out on normal and 'pathological' specimens of Partula species. Although tissue changes and microorganisms were detected, the findings did not suggest that infectious or non-infectious disease contributed significantly to the disease or death of the snails. Additional investigations are suggested.
CENTRAL nervous system disease is often reflected by changes in the composition of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF analysis, although generally a non-specific diagnostic test, can provide vital clues to the cause of neurological disease.
Occipital bone hypoplasia with foramen magnum obstruction and secondary syringomyelia (SM) is a common condition in the Cavalier King Charles Spaniel (CKCS) that is similar to human Chiari type I malformation. A worldwide family tree of more than 5,500 CKCSs spanning a maximum of 24 generations was established by obtaining pedigree information from 120 dogs diagnosed with SM secondary to occipital bone hypoplasia. The ongoing study showed 6 of 8 great grandparents of all affected dogs could be traced back to 2 female ancestors so that all 8 were descended from one or the other or both. The disease appears to be more severe and have an earlier onset with increased inbreeding, especially when breeding from affected dogs. The family tree of idiopathic epilepsy (IE) appears to be a different subset of the CKCS population, although some overlap was observed. Idiopathic epilepsy is more frequent in lines originating from whole-color dogs. Selection for coat color is believed to have influenced the development of both occipital hypoplasia with secondary SM and IE. In addition, breeding guidelines to reduce the incidence of mitral valve disease have placed further pressures on the gene pool.
Nerve biopsy samples from two cats with spontaneously occurring diabetes were examined. The predominant nerve fiber abnormalities observed were restricted to the myelin sheath and Schwann cell. Reactive, degenerative and proliferative Schwann cell changes were evident but the most striking abnormality encountered was splitting and ballooning of the myelin sheath. These observations highlight the significance of Schwann cell injury in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy.
The management of canine epilepsy has to be adjusted to the individual needs of the dog and its owner. In 2015, the International Veterinary Epilepsy Task Force (IVETF) published the "Consensus Proposal: Medical treatment of canine epilepsy in Europe", proposing a systematic therapeutic approach for dogs suffering from idiopathic epilepsy or structural epilepsy. It also gives an overview over antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) licensed for dogs and recommends drug treatment protocols. The consensus proposal is based on current published evidence-based literature, considers the current legal framework in Europe, and reflects the authors' experience. In this article, the contents of the consensus proposal are summarized in German language.
This article, which is based on the PhD thesis of Clare Rusbridge, is a review of chiari-like malformation and syringomyelia in the Cavalier King Charles Spaniel. The abnormality is becoming more common among dwarf breeds and brachychepalic breeds. The nature, prevalence, and treatment of the disease are described, as is current knowledge on its heritability in the Cavalier King Charles Spaniel.
Syringohydromyelia secondary to foramen magnum overcrowding is described in seven Cavalier King Charles spaniels. Clinical signs were consistent with a central spinal cord lesion. The most common signs were persistent scratching at the shoulder region with apparent neck, thoracic limb, or ear pain and thoracic limb lower motor neuron deficits. The diagnosis was made by magnetic resonance imaging. The syringohydromyelia is postulated to be a consequence of an occipital bone malformation resulting in a small caudal fossa and cerebellar herniation. Clinical signs improved but did not completely resolve when the dogs received treatment with corticosteroids or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
The development of a cost-effective surface scanning system tailored for live animal image capture can play an important role in biomedical research. The primary aim was to introduce a low-cost system, achieving a surface reconstruction error of less than 2mm, and enabling rapid acquisition speeds of approximately 1 second for a complete 360-degree surface capture. Leveraging a five RGB-D camera configuration, our approach offers a simple, low-cost alternative to conventional lab-based 3D scanning setups. Key to our methodology is a novel calibration strategy aimed at refining intrinsic and extrinsic camera parameters simultaneously for improved accuracy. We introduce a novel 3D calibration object, extending existing techniques employing ArUco markers, and implement a depth correction matrix to enhance depth accuracy. By utilizing Simulated Annealing optimization alongside our custom calibration object, we achieve superior results compared to conventional optimization techniques. Our obtained results show that the proposed depth correction method can reduce the reprojection error from 3.12 to 2.89 pixels. Furthermore, despite the simplicity of our reconstruction method, we observe around a 22% improvement in surface reconstruction compared to factory calibration parameters. Our findings underscore the practicality and efficacy of our proposed system, paving the way for enhanced 3D surface reconstruction for real-world surface capture.
Abstract Background French bulldogs hospitalised for the management of intervertebral disc extrusion (IVDE) are frequently affected by respiratory compromise, typically brachycephalic‐associated upper respiratory obstruction and/or aspiration events. We evaluated the occurrence of such respiratory compromise events in French bulldogs presented to two referral hospitals. Methods Clinical data for French bulldogs diagnosed with IVDE were retrospectively collated, including severity of neurological deficits, neuroanatomical localisation, diagnosis, details of respiratory compromise, treatment and outcome. Results A total of 306 dogs diagnosed with IVDE were included. Sixty dogs (19.6%) experienced respiratory compromise, of which 31 dogs (10.1%) progressed to cyanosis, collapse or respiratory arrest. Limitations The study was limited by its retrospective nature. Furthermore, the duration of hospitalisation was not evaluated and the decision for euthanasia was often multifactorial. Conclusion One in five French bulldogs presented with IVDE experienced respiratory compromise. The detrimental welfare effects of this warrant further discussion.
UNLABELLED: PRESENTATION AND LESION LOCALISATION: Seven adult domestic shorthair cats were presented with a 1- to 6-day history of progressive neurological signs. A focal skin puncture and subcutaneous swelling over the dorsal part of the head were detected on physical examination. Neurological examination indicated lesion(s) in the right forebrain in four cats, multifocal forebrain in one cat, left forebrain in one cat, and multifocal forebrain and brainstem in the remaining cat. In all cats, magnetic resonance imaging revealed a space-occupying forebrain lesion causing a severe mass effect on adjacent brain parenchyma. CLINICAL APPROACH AND OUTCOME: All cats were managed with a combination of medical and surgical treatment. At surgery a small penetrating calvarial fracture was detected in all cats, and a tooth fragment was found within the content of the abscess in two cats. The combination of surgical intervention, intensive care and intravenous antimicrobials led to a return to normal neurological function in five cats. PRACTICAL RELEVANCE: As this series of cases indicates, successful resolution of a brain abscess due to a bite injury depends on early recognition and combined used of antimicrobials and surgical intervention. A particular aim of surgery is to remove any skull and foreign body (tooth) fragments that may represent a continuing focus of infection.
OBJECTIVES: To ascertain whether cavalier King Charles spaniels (CKCSs) have a proportionately smaller caudal fossa compared with other small dogs and with Labradors. To evaluate if cerebellar herniation in CKCS correlates with caudal fossa volume. METHODS: In this retrospective study, three-dimensional images were created from magnetic resonance imaging brain series of 117 dogs (split into three groups: CKCS, Labradors and small breeds) from which the volumes of the fossae and brain parenchyma were calculated. These volumes were transformed into percentages of total cranial cavity and parenchyma volumes, respectively. The percentages were statistically compared among the groups. The percentage of herniated cerebellum in the CKCS was compared using linear regression with the caudal fossa and parenchyma percentages. RESULTS: Cavalier King Charles spaniels had a proportionately smaller caudal fossa compared with Labradors (P=0.002) but not to small breeds (P=0.103). Their caudal fossa parenchyma was proportionately the same volume as Labradors (P=0.976) but greater than small breeds (P=0.005). No relationship was found for the per cent of cerebellum herniated. CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE: The results support mesoderm insufficiency or craniosynostosis as the pathogenesis of Chiari-like malformation (CM) in CKCS. It presents evidence for overcrowding of the caudal fossa due to a mismatch of brain parenchyma and fossa volumes as to why CKCS and not other small dogs are affected.
Background: The term meningoencephalocele (MEC) describes a herniation of cerebral tissue and meninges through a defect in the cranium, whereas a meningocele (MC) is a herniation of the meninges alone. Hypothesis/Objectives: To describe the clinical features, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) characteristics, and outcomes of dogs with cranial MC and MEC. Animals: Twenty-two client-owned dogs diagnosed with cranial MC or MEC. Methods: Multicentric retrospective descriptive study. Clinical records of 13 institutions were reviewed. Signalment, clinical history, neurologic findings and MRI characteristics as well as treatment and outcome were recorded and evaluated. Results: Most affected dogs were presented at a young age (median, 6.5 months; range, 1 month – 8 years). The most common presenting complaints were seizures and behavioral abnormalities. Intranasal MEC was more common than parietal MC. Magnetic resonance imaging identified meningeal enhancement of the protruded tissue in 77% of the cases. Porencephaly was seen in all cases with parietal MC. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis identified mild abnormalities in 4 of 11 cases. Surgery was not performed in any affected dog. Seventeen patients were treated medically, and seizures were adequately controlled with anti-epileptic drugs in 10 dogs. Dogs with intranasal MEC and mild neurologic signs had a fair prognosis with medical treatment. Conclusion and clinical importance: Although uncommon, MC and MEC should be considered as a differential diagnosis in young dogs presenting with seizures or alterations in behavior. Medical treatment is a valid option with a fair prognosis when the neurologic signs are mild.
OBJECTIVES: To investigate the possible association between caudal fossa area and cervical vertebral dimensions and the presence of syringomyelia in cavalier King Charles spaniels. METHODS: From magnetic resonance imaging scans of 78 cavalier King Charles spaniels, measurements were made of the widest vertical spinal width at C1/C2, C2, C2/C3 and C3; angulation of the C2/C3 spine; and estimated caudal fossa area. A correlation between these measurements and syringomyelia was sought. RESULTS: A total of 59 dogs with and 19 without syringomyelia were compared. Older dogs had a significantly higher incidence of syringomyelia. No difference in incidence was noted between genders. There was no significant difference in vertebral canal width at C1/C2 and C2, or angulation of C2/C3 between syringomyelia and non-syringomyelia groups. The width of the canal at C2/C3 and C3 was significantly increased in syringomyelia dogs. There was no significant difference in the caudal fossa area between groups. CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE: Although syringomyelia was shown to be more prevalent in older dogs, the age beyond which dogs were considered at greater risk was not deducible from the dataset. The association identified between wider spinal canal at C3, and C2/C3 and syringomyelia presence is of questionable clinical significance, as the difference between syringomyelia and non-syringomyelia groups is too small to be measured in a clinical setting.
Syringomyelia is a common and chronic neurological disorder affecting Cavalier King Charles Spaniels. The condition is putatively painful, but evaluating the affective component of chronic pain in non-human animals is challenging. Here we employed two methods designed to assess animal affect – the judgement bias and reward loss sensitivity tests – to investigate whether Cavalier King Charles Spaniels with syringomyelia (exhibiting a fluid filled cavity (syrinx) in the spinal cord of ≥2mm diameter) were in a more negative affective state than those without the condition. Dogs with syringomyelia did not differ in age from those without the condition, but owners reported that they scratched more (P
This study aimed to develop a system of quantitative analysis of canine Chiari-like malformation and syringomyelia on variable quality MRI. We made a series of measurements from magnetic resonance DICOM images from Griffon Bruxellois dogs with and without Chiari-like malformation and syringomyelia and identified several significant variables. We found that in the Griffon Bruxellois dog, Chiari-like malformation is characterized by an apparent shortening of the entire cranial base and possibly by increased proximity of the atlas to the occiput. As a compensatory change, there appears to be an increased height of the rostral cranial cavity with lengthening of the dorsal cranial vault and considerable reorganization of the brain parenchyma including ventral deviation of the olfactory bulbs and rostral invagination of the cerebellum under the occipital lobes.
A 10‐month‐old male Labrador retriever was presented for acute onset altered mentation and inability to walk. The dog was presented with a modified glasgow coma scale (MGCS) of 12 with tachycardia (148 bpm) and hypothermia (37°C). The dog had been normal the previous night then found semi‐comatose at the following morning. Investigations included haematology, biochemistry, C‐reactive protein, magnetic resonance imaging, urine toxicology and cerebrospinal fluid analysis. Ten hours after being found the dog passed faeces containing a significant volume of berries. The owner later determined that 750 g of sloe berries soaked in gin were missing from the garden compost heap. Serum ethanol concentrations measured approximately 20 hours after the suspected consumption were 310 mgD/L. The dog was treated with intralipid, intravenous fluid therapy and paracetamol. He was neurologically normal (MGCS = 0) 24 hours later, following diagnosis and treatment. Differential diagnosis and management of the comatose dog and management of ethanol toxicity are discussed.
Tabby patterns of fur coats are defining characteristics in wild and domestic felids. Historically, three autosomal alleles at one locus (Tabby): Abyssinian (Ta; a.k.a. ticked), mackerel (Tm; a.k.a. striped) and blotched (tb; a.k.a. classic, blotched) were thought to control these patterns in domestic cats and their breeds. Currently, at least three loci influence cat tabby markings, two of which are designated Tabby and Ticked. The Tabby locus is laeverin (LVRN) and affects the mackerel and blotched patterns. The unidentified gene for the Ticked locus on cat chromosome B1 was suggested to control the presence or absence of the ticked pattern (Tabby – Abyssinian (Ta; a.k.a. ticked). The cat reference genome (Cinnamon, the Abyssinian) has the ticked phenotype and the variant dataset and coat phenotypes from the 99 Lives Cat Genome Consortium (195 cats) were used to identify candidate genes and variants associated with the Ticked locus. Two strategies were used to find the Ticked allele(s), one considered Cinnamon with the reference allele or heterozygous (Strategy A) and the other considered Cinnamon as having the variant allele or heterozygous (Strategy B). For Strategy A, two variants in Dickkopf Wnt Signaling Pathway Inhibitor 4 (DKK4), a p.Cys63Tyr (B1:41621481, c.188G>A) and a less common p.Ala18Val (B1:42620835, c.53C>T) variant are suggested as two alleles influencing the Ticked phenotype. Bioinformatic and molecular modeling analysis suggests that these changes disrupt a key disulfide bond in the Dkk4 cysteine‐rich domain 1 or Dkk4 signal peptide cleavage respectively. All coding variants were excluded as Ticked alleles using Strategy B.
The causes of clinical signs associated with syringomyelia in the Cavalier King Charles Spaniel (CKCS) are incompletely understood. In this study we compared expression of two pain-related neuropeptides: substance P (SP) and calcitonin gene related peptide (CGRP), in the spinal cord dorsal horn of normal dogs with that in CKCS with and without clinical signs of syringomyelia. There was a decrease in expression of both peptides in CKCS with 'symptomatic' syringomyelia that was also associated with significant asymmetry in SP-I and similar, though non-significant, asymmetry in CGRP-I compared with other groups. The asymmetric distribution of these pain-related peptides may be a consequence of syrinx-associated damage to grey matter but may also play a role in generation of pain.
BackgroundSome paroxysmal movement disorders remain without an identified genetic cause. ObjectivesThe aim was to identify the causal genetic variant for a paroxysmal dystonia-ataxia syndrome in Weimaraner dogs. MethodsClinical and diagnostic investigations were performed. Whole genome sequencing of one affected dog was used to identify private homozygous variants against 921 control genomes. ResultsFour Weimaraners were presented for episodes of abnormal gait. Results of examinations and diagnostic investigations were unremarkable. Whole genome sequencing revealed a private frameshift variant in the TNR (tenascin-R) gene in an affected dog, XM_038542431.1:c.831dupC, which is predicted to truncate more than 75% of the open read frame. Genotypes in a cohort of 4 affected and 70 unaffected Weimaraners showed perfect association with the disease phenotype. ConclusionsWe report the association of a TNR variant with a paroxysmal dystonia-ataxia syndrome in Weimaraners. It might be relevant to include sequencing of this gene in diagnosing humans with unexplained paroxysmal movement disorders. (c) 2023 The Authors. Movement Disorders published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Orthostatic tremor (OT) is a rare movement disorder characterized by high-frequency (>12 Hz) involuntary, rhythmic, sinusoidal movements affecting predominantly the limbs while standing. To describe the signalment, presenting complaints, phenotype, diagnostic findings, treatment, and outcome of a large sample of dogs with OT. Sixty dogs diagnosed with OT based on conscious electromyography. Multicenter retrospective case series study. Dogs were included if they had a conscious electromyography consistent with muscle discharge frequency >12 Hz while standing. Fifty-three cases were diagnosed with primary OT (POT). Giant breed dogs represented most cases (83%; 44/53). Most dogs (79%; 42/53) were younger than 2 years of age at onset of signs, except for Retrievers which were all older than 3.5 years of age. The most common presenting complaints were pelvic limb tremors while standing (85%; 45/53) and difficulty when rising or sitting down (45%; 24/53). Improvement of clinical signs occurred in most dogs (85%; 45/53) treated medically with phenobarbital, primidone, gabapentin, pregabalin or clonazepam, but it was mostly partial rather than complete. Orthostatic tremor-plus was seen in 7 dogs that had concurrent neurological diseases. Primary OT is a progressive disease of young, purebred, giant/large-breed dogs, which appears to begin later in life in Retrievers. Primary OT apparently responds partially to medications. Orthostatic tremor-plus exists in dogs and can be concomitant or associated with other neurological diseases.
In this chapter, our current understanding of the mechanisms causing neuropathic pain and the nonsurgical therapy of syringomyelia are reviewed. Traditional pharmacological therapies such as tricyclic antidepressants, serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitors, antiepileptic drugs, opioids and NMDA receptor antagonists are detained, together with novel drug therapies such as cannabis, endocannabinoids and naltrexone. Management strategies for central neuropathic pain are suggested, including combination therapy, topical analgesics and intrathecal infusions. Limitations of therapy are discussed, together with likely future directions for treatment. Non-pharmacological treatments, such as acupuncture, complementary medicine, cognitive therapy and neurostimulation, are also considered.
Canine idiopathic epilepsy has an estimated prevalence of 0.62 per cent in primary veterinary practice (Kearsley-Fleet and others 2013) and as such is one of the most common chronic neurological diseases. Descriptions of ‘epilepsy of unknown origin . . . where no symptom characteristic of any other condition has as yet presented’ can be found in early veterinary textbooks (Kirk 1922) and although our knowledge is now considerably greater, and we are no longer treating it with arsenic, we are still a long way from preventing or curing this enigmatic disease. This article describes the diagnosis, management and considerations to take when dealing with this condition.
A patient once remarked about how a certain individual, by the name of Arnold Chiari, had affected her and her family’s life. This serves to remind us that it might sometimes be helpful if doctors could find time to explain to their patients not only the meaning of the term Arnold-Chiari malformation but also its origins.
Objectives:To characterize and compare the phenotypic variables of the hindbrain and craniocervical junction associated with syringomyelia (SM) in the Chihuahua, Affenpinscher and Cavalier King Charles Spaniel (CKCS). Method Analysis of 273 T1-weighted mid-sagittal DICOM sequences of the hindbrain and craniocervical junction from 99 Chihuahuas, 42 Affenpinschers and 132 CKCSs. The study compared 22 morphometric features (11 lines, eight angles and three ratios) of dogs with and without SM using refined techniques based on previous studies of the Griffon Bruxellois (GB) using Discriminant Function Analysis and ANOVA with post-hoc corrections. Results The analysis identified 14/22 significant traits for SM in the three dog breeds, five of which were identical to those reported for the GB and suggest inclusion of a common aetiology. One ratio, caudal fossa height to the length of the skull base extended to an imaginary point of alignment between the atlas and supraoccipital bones, was common to all three breeds (p values 0.029 to
Recent work identified anti-GM2 and anti-GalNAc-GD1a IgG ganglioside antibodies as biomarkers in dogs clinically diagnosed with acute canine polyradiculoneuritis, in turn considered a canine equivalent of Guillain-Barré syndrome. This study aims to investigate the serum prevalence of similar antibodies in cats clinically diagnosed with immune-mediated polyneuropathies. The sera from 41 cats clinically diagnosed with immune-mediated polyneuropathies (IPN), 9 cats with other neurological or neuromuscular disorders (ONM) and 46 neurologically normal cats (CTRL) were examined for the presence of IgG antibodies against glycolipids GM1, GM2, GD1a, GD1b, GalNAc-GD1a, GA1, SGPG, LM1, galactocerebroside and sulphatide. A total of 29/41 IPN-cats had either anti-GM2 or anti-GalNAc-GD1a IgG antibodies, with 24/29 cats having both. Direct comparison of anti-GM2 (sensitivity: 70.7%; specificity: 78.2%) and anti-GalNAc-GD1a (sensitivity: 70.7%; specificity: 70.9%) antibodies narrowly showed anti-GM2 IgG antibodies to be the better marker for identifying IPN-cats when compared to the combined ONM and CTRL groups (P = .049). Anti-GA1 and/or anti-sulphatide IgG antibodies were ubiquitously present across all sample groups, whereas antibodies against GM1, GD1a, GD1b, SGPG, LM1 and galactocerebroside were overall only rarely observed. Anti-GM2 and anti-GalNAc-GD1a IgG antibodies may serve as serum biomarkers for immune-mediated polyneuropathies in cats, as previously observed in dogs and humans.
Background Non‐traumatic spinal cord hemorrhage (NTSH) is an uncommon cause of myelopathy in dogs. Objectives Describe the clinical characteristics, concurrent medical conditions and underlying causes, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings and outcome in dogs with NTSH. Animals Dogs diagnosed with NTSH using gradient echo T2‐weighted (GRE) sequences with or without histopathological confirmation of hemorrhage were included. Dogs with a traumatic cause were excluded, including those with compressive intervertebral disc extrusion. Methods Retrospective descriptive study; the databases of 2 referral hospitals were searched between 2013 and 2021. Results Twenty‐three dogs met inclusion criteria. The onset of signs was acute and progressive in 70% of cases; spinal hyperesthesia was variable (48%). Hemorrhage was identified in the thoracolumbar spinal segments in 65% of dogs. An underlying cause was identified in 65% of cases. Angiostrongylus vasorum represented 18% of the total cohort, followed by steroid‐responsive meningitis arteritis (SRMA; 13%). Overall, 64% of dogs had a good or excellent outcome, regardless of cause; which was increased to 100% for SRMA, 75% for A. vasorum and 75% for idiopathic NTSH. Outcome was not associated with neurological severity. Recovery rate was 67% and 50% for nociception‐intact and nociception‐negative dogs, respectively. Conclusions Larger prospective studies would be required to define prognostic factors for dogs with NTSH, but outcome appeared to be most influenced by the underlying cause, as opposed to neurological severity at presentation.
Kinesin-2 enables ciliary assembly and maintenance as an anterograde intraflagellar transport (IFT) motor. Molecular motor activity is driven by a heterotrimeric complex comprised of KIF3A and KIF3B or KIF3C plus one non-motor subunit, KIFAP3. Using exome sequencing, we identified heterozygous KIF3B variants in two unrelated families with hallmark ciliopathy phenotypes. In the first family, the proband presents with hepatic fibrosis, retinitis pigmentosa, and postaxial polydactyly; he harbors a de novo c.748G>C (p.Glu250Gln) variant affecting the kinesin motor domain encoded by KIF3B. The second family is a six-generation pedigree affected predominantly by retinitis pigmentosa. Affected individuals carry a heterozygous c.1568T>C (p.Leu523Pro) KIF3B variant segregating in an autosomal-dominant pattern. We observed a significant increase in primary cilia length in vitro in the context of either of the two mutations while variant KIF3B proteins retained stability indistinguishable from wild type. Furthermore, we tested the effects of KIF3B mutant mRNA expression in the developing zebrafish retina. In the presence of either missense variant, rhodopsin was sequestered to the photoreceptor rod inner segment layer with a concomitant increase in photoreceptor cilia length. Notably, impaired rhodopsin trafficking is also characteristic of recessive KIF3B models as exemplified by an early-onset, autosomal-recessive, progressive retinal degeneration in Bengal cats; we identified a c.1000G>A (p.Ala334Thr) KIF3B variant by genome-wide association study and whole-genome sequencing. Together, our genetic, cell-based, and in vivo modeling data delineate an autosomal-dominant syndromic retinal ciliopathy in humans and suggest that multiple KIF3B pathomechanisms can impair kinesin-driven ciliary transport in the photoreceptor.
Case summary A 10-year-old male neutered Russian Blue cat was presented with a 2-month history of progressive non-ambulatory paraparesis. Spinal MRI revealed a well-demarcated, compressive intradural extramedullary mass at the level of T1 vertebra. The mass had subtle hyperintensity on T2-weighted images, was isointense on T1-weighted images and had diffuse, marked enhancement following gadolinium administration. Neuroaxis MRI, including limited brain sequences, excluded other visible lesions. Thoracic and abdominal radiographs were unremarkable. The mass was resected via a dorsal C7-T2 laminectomy and durotomy. Histopathology revealed a neoplasm composed of columnar-to-polygonal cells forming bilayered palisading patterns with a few apical cilia. Three mitoses were noted in 10 high-power fields. This was consistent with an epithelial neoplasm and initially a metastatic adenocarcinoma was considered most likely. Full-body CT with contrast and including the brain found rhinitis but did not identify any additional neoplastic foci. Biopsies of the nasal cavity and fine-needle aspiration of the spleen and liver were unremarkable. On immunohistochemical evaluation, pan-cytokeratin and E-cadherin immunolabelling was observed; however, synaptophysin, thyroglobulin, chromogranin A and glial fibrillary acidic protein was not detected. This, along with the histological morphology and absence of a primary tumour, was compatible with an ectopic choroid plexus neoplasm. Follow-up performed at 3, 14 and 24 months postoperatively revealed neurological improvement without recurrence. Relevance and novel information We describe the presentation, histopathological and immunohistochemical features and outcome of a case of a rare ectopic choroid plexus neoplasm in the spinal cord of a cat.
Background Myoclonus is observed in older Cavalier King Charles Spaniels (CKCS) but a full description is lacking. Objectives The presence, age of onset, characteristics and treatment of myoclonic episodes were retrospectively evaluated in a cohort of CKCS which presented to 1 board-certified neurologist. Clinical data, imaging studies, presence of seizures and their management, as well as other comorbidities were noted. Animals Thirty-nine CKCS that were presented to 2 institutions between 2001 and 2018 with signs consistent with myoclonus. Clinical examination, blood sampling, advanced diagnostic imaging, cerebrospinal fluid analysis, and record keeping of other comorbidities was performed. Methods This is a retrospective case series, describing the presence of myoclonus in CKCS. Results Clinical signs reported were spontaneous in onset, lasted a few seconds and consisted of rapid blinking with head nodding and variable extension down the thoracic limbs. Myoclonus occasionally led to stumbling of the thoracic limbs or collapse. Mean age of onset was 8.38 years (SD +/- 1.96). Thirteen of 39 dogs with myoclonus had paroxysmal events, such as generalized seizures (9/13). Conclusions and Clinical Importance Myoclonus occurs in middle-aged to older CKCS and seems to be another epiphenomena of this breed. A link to epilepsy might be present.
A previous single-country pilot study indicated serum anti-GM2 and anti-GA1 anti-glycolipid antibodies as potential biomarkers for acute canine polyradiculoneuritis. This study aims to validate these findings in a large geographically heterogenous cohort. Sera from 175 dogs clinically diagnosed with acute canine polyradiculoneuritis, 112 dogs with other peripheral nerve, cranial nerve or neuromuscular disorders and 226 neurologically normal dogs were screened for anti-glycolipid antibodies against 11 common glycolipid targets to determine the immunoglobulin G anti-glycolipid antibodies with the highest combined sensitivity and specificity for acute canine polyradiculoneuritis. Anti-GM2 anti-glycolipid antibodies reached the highest combined sensitivity and specificity (sensitivity: 65.1%, 95% confidence interval 57.6 to 72.2%; specificity: 90.2%, 95% confidence interval 83.1 to 95.0%), followed by anti-GalNAc-GD1a anti-glycolipid antibodies (sensitivity: 61.7%, 95% confidence interval 54.1 to 68.9%; specificity: 89.3%, 95% confidence interval 82.0 to 94.3%) and these anti-glycolipid antibodies were frequently present concomitantly. Anti-GA1 anti-glycolipid antibodies were detected in both acute canine polyradiculoneuritis and control animals. Both for anti-GM2 and anti-GalNAc-GD1a anti-glycolipid antibodies, sex was found a significantly associated factor with a female to male odds ratio of 2.55 (1.27 to 5.31) and 3.00 (1.22 to 7.89), respectively. Anti-GalNAc-GD1a anti-glycolipid antibodies were more commonly observed in dogs unable to walk (OR 4.56, 1.56 to 14.87). Anti-GM2 and anti-GalNAc-GD1a immunoglobulin G anti-glycolipid antibodies represent serum biomarkers for acute canine polyradiculoneuritis.
Case summary A 10-year-old male neutered domestic shorthair cat was presented with a 5-month history of progressive non-ambulatory paraparesis. Initial vertebral column radiographs revealed an L2-L3 expansile osteolytic lesion. Spinal MRI showed a well-demarcated, compressive expansile extradural mass lesion affecting the caudal lamina, caudal articular processes and right pedicle of the second lumbar vertebra. The mass was hypointense/isointense on T2-weighted images, isointense on T1-weighted images and had mild homogeneous contrast enhancement after gadolinium administration. MRI of the remaining neuroaxis and CT of the neck, thorax and abdomen with ioversol contrast revealed no additional neoplastic foci. The lesion was removed by en bloc resection via a dorsal L2-L3 laminectomy, including the articular process joints and pedicles. Vertebral stabilisation was performed with titanium screws placed within L1, L2, L3 and L4 pedicles with polymethylmethacrylate cement embedding. Histopathology revealed an osteoproductive neoplasm composed of spindle and multinucleated giant cells without detectable cellular atypia or mitotic activity. On immunohistochemical evaluation, osterix, ionised calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1 and vimentin labelling were observed. Based on the clinical and histological features, a giant cell tumour of bone was considered most likely. Follow-up at 3 and 24 weeks postoperatively demonstrated significant neurological improvement. Postoperative full-body CT at 6 months showed instability of the stabilisation construct but absence of local recurrence or metastasis.Relevance and novel information This is the first reported case of a giant cell tumour of bone in the vertebra of a cat. We present the imaging findings, surgical treatment, histopathology, immunohistochemistry and outcome of this rare neoplasm.
An inherited neurologic syndrome in a family of mixed-breed Oriental cats has been characterized as forebrain commissural malformation, concurrent with ventriculomegaly and interhemispheric cysts. However, the genetic basis for this autosomal recessive syndrome in cats is unknown. Forty-three cats were genotyped on the Illumina Infinium Feline 63K iSelect DNA Array and used for analyses. Genome-wide association studies, including a sib-transmission disequilibrium test and a case-control association analysis, and homozygosity mapping, identified a critical region on cat chromosome A3. Short-read whole genome sequencing was completed for a cat trio segregating with the syndrome. A homozygous 7 bp deletion in growth differentiation factor 7 ( GDF7 ) (c.221_227delGCCGCGC [p.Arg74Profs]) was identified in affected cats, by comparison to the 99 Lives Cat variant dataset, validated using Sanger sequencing and genotyped by fragment analyses. This variant was not identified in 192 unaffected cats in the 99 Lives dataset. The variant segregated concordantly in an extended pedigree. In mice, GDF7 mRNA is expressed within the roof plate when commissural axons initiate ventrally-directed growth. This finding emphasized the importance of GDF7 in the neurodevelopmental process in the mammalian brain. A genetic test can be developed for use by cat breeders to eradicate this variant.
All domesticated mammals exhibit marked reductions in overall brain size, however, it is unknown whether the corpus callosum, an integral white matter fiber pathway for interhemispheric cortical communication, is affected by domestication differentially or strictly in coordination with changes in brain size. To answer this question, we used quantitative magnetic resonance imaging to compare the mid‐sagittal cross‐sectional areas of the corpus callosum in 35 carnivore species, including eight wild canids and 13 domestic dogs. We segmented rostro‐caudal regions of interest for the corpus callosum and evaluated correlations with brain mass. The results of this study indicate that under the influence of domestication in canids, the corpus callosum scales to brain size in an allometric relationship that is similar to that of wild canids and other carnivores, with relatively high correlation coefficients observed for all regions, except the rostrum. These results indicate that architectural and energetic considerations are likely to tightly constrain variation in caudal components of the corpus callosum relative to overall brain size, however fibers passing through the rostrum, putatively connecting prefrontal cortex, are less constrained and therefore may contribute more towards species‐specific differences in connectivity. Given the species diversity of the Canidae and the resurgence of interest in the brain of the domestic dog, further studies aimed at characterizing the neural architecture in domesticated species is likely to provide new insights into the effects of domestication, or artificial selection, on the brain.
Background: Feline idiopathic ulcerative dermatosis is a rare, poorly understood condition characterized by self-trauma. The lesion presents as a nonhealing, crusted ulcer, which occurs most commonly on the dorsal midline of the neck or between the scapulae. Animal: A 2-year-old female neutered domestic short hair cat was presented with an ulcerative dermatosis affecting the dorsal midline. Previous investigations had failed to identify the cause, and the lesion was resistant to treatment. Methods and results: Diagnosis was based on clinical findings and confirmed by histopathology showing epidermal ulceration and superficial necrosis with a mild dermal infiltrate together with subepidermal fibrosis. The cat had been fed a commercial hypoallergenic diet for 6 months, which had successfully managed its chronic diarrhoea. Deep skin scrapings, cytology and fungal culture failed to demonstrate pathogens. Conclusions and clinical importance: Remission was obtained within 4 weeks and has been maintained over a 30 month period with topiramate (5 mg/kg orally twice daily), an anti-epileptic drug used in human medicine. Attempts to withdraw this therapy led to relapse within 24 h on two occasions. To the best of the authors' knowledge, this is the first case report of the use of this drug for feline idiopathic ulcerative dermatosis. © 2014 ESVD and ACVD.
Ilona Rodan, Sarah Heath. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 6. 7. 8. 9. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. PART The Cat in the Veterinary Practice Physiologic and Diagnostic. (MEMO) in the management of cats with idiopathic cystitis.
Chiari-like malformation (CM) and syringomyelia (SM) is an important disease complex in the Cavalier King Charles Spaniel (CKCS) but data about the anatomical distribution of SM along the spinal cord are lacking in veterinary medicine. The objective of this study was to define the anatomic distribution of SM in CKCS clinically affected by CM/SM. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain and the entire spinal cord of 49 dogs was performed and different morphological parameters compared. Syrinx formation was present in the C1-C4 region and in other parts of the spinal cord. The maximal dorsoventral syrinx size can occur in any region of the spinal cord and the total syrinx size was positively correlated with age. Seventy-six per cent of CKCS with a cranial cervical syrinx also have a syrinx affecting more caudal spinal cord regions. MRI restricted to the cervical region may underestimate the extent of SM and the severity of the disease process in the majority of dogs.
Inflammatory cytokines are potential modulators of infarct progression in acute ischaemic stroke, and are therefore possible targets for future treatment strategies. Cytokine studies in animal models of surgically induced stroke may, however, be influenced by the fact that the surgical intervention itself contributes towards the cytokine response. Community-dwelling domestic dogs suffer from spontaneous ischaemic stroke, and therefore, offer the opportunity to study the cytokine response in a noninvasive set-up. The aims of this study were to investigate cytokine concentrations in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in dogs with acute ischaemic stroke and to search for correlations between infarct volume and cytokine concentrations. Blood and CSF were collected from dogs less than 72 h after a spontaneous ischaemic stroke. Infarct volumes were estimated on MRIs. Interleukin (IL)-2, IL-6, IL- 8, IL-10 and tumour necrosis factor in the plasma, CSF and brain homogenates were measured using a canine-specific multiplex immunoassay. IL-6 was significantly increased in plasma (P=0.04) and CSF (P=0.04) in stroke dogs compared with healthy controls. The concentrations of other cytokines, such as tumour necrosis factor and IL-2, were unchanged. Plasma IL-8 levels correlated significantly with infarct volume (Spearman’s r=0.8, P=0.013). The findings showed increased concentrations of IL-6 in the plasma and CSF of dogs with acute ischaemic stroke comparable to humans. We believe that dogs with spontaneous stroke offer a unique, noninvasive means of studying the inflammatory processes that accompany stroke while reducing confounds that are unavoidable in experimental models.
Feline orofacial pain syndrome (FOPS) is a pain disorder of cats with behavioural signs of oral discomfort and tongue mutilation. This report describes the findings from a case series of 113 cats including 100 Burmese. FOPS is suspected to be a neuropathic pain disorder and the predominance within the Burmese cat breed suggests an inherited disorder, possibly involving central and/or ganglion processing of sensory trigeminal information. The disease is characterised by an episodic, typically unilateral, discomfort with pain-free intervals. The discomfort is triggered, in many cases, by mouth movements. The disease is often recurrent and with time may become unremitting - 12% of cases in this series were euthanased as a consequence of the condition. Sensitisation of trigeminal nerve endings as a consequence of oral disease or tooth eruption appears to be an important factor in the aetiology - 63% of cases had a history of oral lesions and at least 16% experienced their first sign of discomfort during eruption of permanent teeth. External factors can also influence the disease as FOPS events could be directly linked to a situation causing anxiety in 20% of cats. FOPS can be resistant to traditional analgesics and in some cases successful management required anti-convulsants with an analgesic effect.
This article, which is based on the PhD thesis of Clare Rusbridge, is a review of chiari-like malformation and syringomyelia in the Cavalier King Charles Spaniel. The abnormality is becoming more common among dwarf breeds and brachychepalic breeds. The nature, prevalence, and treatment of the disease are described, as is current knowledge on its heritability in the Cavalier King Charles Spaniel.
The development of high throughput SNP genotyping technologies has improved the genetic dissection of simple and complex traits in many species including cats. The properties of feline 62,897 SNPs Illumina Infnium iSelect DNA array are described using a dataset of over 2,000 feline samples, the most extensive to date, representing 41 cat breeds, a random bred population, and four wild felid species. Accuracy and efciency of the array’s genotypes and its utility in performing population-based analyses were evaluated. Average marker distance across the array was 37,741 Kb, and across the dataset, only 1% (625) of the markers exhibited poor genotyping and only 0.35% (221) showed Mendelian errors. Marker polymorphism varied across cat breeds and the average minor allele frequency (MAF) of all markers across domestic cats was 0.21. Population structure analysis confrmed a Western to Eastern structural continuum of cat breeds. Genome-wide linkage disequilibrium ranged from 50–1,500 Kb for domestic cats and 750 Kb for European wildcats (Felis silvestris silvestris). Array use in trait association mapping was investigated under diferent modes of inheritance, selection and population sizes. The efcient array design and cat genotype dataset continues to advance the understanding of cat breeds and will support monogenic health studies across feline breeds and populations.
Abstract Background There have been anecdotal reports of episodic involuntary movements in the Border Terrier dog breed for over a decade. Recently, it has been hypothesized that this condition may be a form of paroxysmal dystonic choreoathetosis. The aim of this study was to characterize the phenomenology and clinical course of this condition and compare it to known human movement disorders. Methods Data were collected retrospectively from clinical cases treated by veterinary neurologists and additional information was collected prospectively with an ad-hoc online survey directed to owners of affected dogs. Results The episodes are characterized by generalized dystonia, tremors, titubation, and, in some cases, autonomic signs, such as salivation and vomiting. The median age at onset of the episodes was 3 years and the interval between clusters of episodes could last several months. Most of the episodes occurred from rest, and 67% of the owners reported that the episodes were associated with a trigger, most often excitement. Some owners reported an improvement after changing their dog's diet. We hypothesize that the Border Terrier attacks represent a form of paroxysmal nonkinesigenic dyskinesia. Conclusions The finding of a dystonia phenotype within an inbred population suggests a genetic predisposition, and elucidating the genetic cause could facilitate improved understanding of dystonia. This genetic predisposition and the effect of treatment with anticonvulsant drugs and dietary changes on the severity of the paroxysms warrant further investigation on this condition.
Syringomyelia (SM) in Cavalier King Charles spaniels (CKCSs) is identified commonly on magnetic resonance images and is sometimes associated with clinical signs of pain and cervical hyperaesthesia. However, the mechanism by which SM develops in this breed has not been fully elucidated and the associated effects on spinal cord structure have not been reported previously. The aims of this study were to describe changes found in the spinal cord of CKCSs, to compare findings between symptomatic and asymptomatic dogs and to determine whether syrinx formation was associated with tissue destruction. Anomalies of the central canal were found in all specimens and many dogs had grossly visible fluid-filled cavities within the spinal cord. Prominent microscopical findings were spongy degenerative changes associated with neuronal necrosis and Wallerian degeneration. The ependyma was discontinuous in many specimens, notably in symptomatic individuals, and there was evidence of angiogenesis and fibrous tissue proliferation around blood vessels adjacent to syrinx cavities. Compared with two different samples of the normal dog population, dogs with syrinxes had significantly less grey matter, although this decrease was associated with generalized loss of spinal cord area. Therefore, SM is associated with degenerative changes in the spinal cord and may develop through primary disruption of ependymal integrity followed by vascular hypertrophy and proliferation. Glial and fibrous proliferation appears to be associated with expression of clinical signs.
Background: Chiari-like malformation (CM) and syringomyelia (SM) are widely reported in Cavalier King Charles Spaniels and Griffon Bruxellois dogs. Increasing evidence indicates that CM and SM also occur in other small and toy breed dogs, such as Chihuahuas. Objectives: To describe the presence of SM and craniocervical junction (CCJ) abnormalities in Chihuahuas and to evaluate the possible association of CCJ abnormalities with SM. To describe CM/SM-related clinical signs and neurologic deficits and to investigate the association of CM/SM-related clinical signs with signalment, SM, or CCJ abnormalities. Animals: Fifty-three client-owned Chihuahuas. Methods: Prospective study. Questionnaire analyses and physical and neurologic examinations were obtained before magnetic resonance and computed tomography imaging. Images were evaluated for the presence of SM, CM, and atlantooccipital overlapping. Additionally, medullary kinking, dorsal spinal cord compression, and their sum indices were calculated. Results: Scratching was the most common CM/SM-related clinical sign and decreased postural reaction the most common neurologic deficit in 73 and 87% of dogs, respectively. Chiari-like malformation and SM were present in 100 and 38% of dogs, respectively. Syringomyelia was associated with the presence of CM/SM-related clinical signs (P = 0.034), and medullary kinking and sum indices were higher in dogs with clinical signs (P = 0.016 and P = 0.007, respectively). Conclusions and Clinical Importance: Syringomyelia and CCJ abnormalities are prevalent in Chihuahuas. Syringomyelia was an important factor for the presence of CM/SM-related clinical signs, but many dogs suffered from similar clinical signs without being affected by SM, highlighting the clinical importance of CCJ abnormalities in Chihuahuas.
Chiari-like Malformation (CM) and secondary syringomyelia (SM), as well as their analogous human conditions, is a complex developmental condition associated with pain and accompanying welfare concerns. CM/SM is diagnosed ever more frequently, thanks in part to the increased availability of magnetic resonance imaging in veterinary medicine. Research over the last two decades has focused primarily on its pathophysiology relating to overcrowding of the cranial caudal fossa. More recent characterizations of CM/SM include brachycephaly with osseous reduction and neural parenchymal displacement involving the entire brain and craniocervical junction to include rostral flattening, olfactory bulb rotation, increased height of the cranium, reduced cranial base with spheno-occipital synchondrosis angulation, reduced supraoccipital and interparietal crest and rostral displacement of the axis and atlas with increased odontoid angulation. The most shared manifestation of CM is the development of fluid-filled pockets (syrinx, syringes) in the spinal cord that can be readily quantified. Dogs with symptomatic CM without SM have a reduced basioccipital bone, compensatory increased cranial fossa height with displaced parenchyma whereby the cerebellum is invaginated beneath the occipital lobes but without compromising cerebrospinal fluid channels enough to cause SM. Thus, broadly defined, CM might be described as any distortion of the skull and craniocervical junction which compromises the neural parenchyma and cerebrospinal fluid circulation causing pain and/or SM. The etiology of CM is multifactorial, potentially including genetically-influenced, breed-specific abnormalities in both skeletal and neural components. Since causation between specific morphologic changes and SM or clinical signs is unproven, CM might be more appropriately considered as a brachycephalic obstructive CSF channel syndrome (BOCCS) rather than a single malformation. Understanding the normal development of the brain, skull and craniocervical junction is fundamental to identifying deviations which predispose to CM/SM. Here we review its anatomical, embryological, bio-mechanical, and genetic underpinnings to update the profession’s understanding of this condition and meaningfully inform future research to diminish its welfare impact.
Background: Breed-specific and broader cohort studies have shown behavioural changes in dogs following the onset of idiopathic epilepsy (IE). Methods: A cross-sectional, case–control questionnaire study was carried out to strengthen this body of evidence. Owners of eight breeds of dog completed an online questionnaire about their dogs’ behaviour; once for control dogs and twice for dogs with IE, for both pre-IE and post-IE onset behaviour. Results: Ninety-six (24.74 per cent) dogs with IE and 292 (75.26 per cent) age and breed-matched control dogs met the inclusion criteria. Control dogs had significantly higher ‘Trainability’ scores than dogs with IE (P=0.04). After IE, dogs had significantly higher ‘Dog-Directed Fear or Aggression’ (P=0.02), ‘Non-Social Fear’ (P=0.01), ‘Attachment/Attention-Seeking Behaviour’ (P=0.04), ‘Attention-Deficit’ (P=0.02) and significantly lower ‘Trainability’ (P=0.02) than prior to the onset of IE. Medication status did not significantly affect any behavioural factor, but drug-resistant dogs had significantly less ‘Trainability’ than drug-responsive (P=0.04) and partially drug-responsive dogs (P=0.03). Conclusion: Behavioural differences related to cognitive function are seen between dogs with IE and controls. Behavioural changes related to anxiety, attention and cognition are seen in dogs following the onset of IE. The ability to clinically define and diagnose behavioural comorbidities in dogs is much needed from both a clinical and research perspective.
A 10-year-old female neutered domestic shorthair (DSH) cat and a 6-year-old female neutered Siamese cat were presented following a peracute onset of decerebellate rigidity and a cerebellar vestibular syndrome, respectively. In both cats, physical examination and routine blood tests were unremarkable, as was routine analysis of cerebrospinal fluid obtained from the DSH cat. Based on the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) features - focal wedge-shaped lesion in the cerebellum characterised by hyperintensity in T2-weighted, T2( *)-gradient echo and fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) images - a presumptive diagnosis of cerebellar infarct was made in both cases. In the DSH cat, the post-mortem examination confirmed the diagnosis of cerebellar infarct and additionally found acute renal infarcts and a pulmonary neoplasia. In the Siamese cat, ultrasonographic evaluation of the heart revealed a probable low-grade chronic valvular endocarditis which was thought to be a potential source of thromboembolism. This paper describes the first two cases - one confirmed and the other suspected - of cerebellar infarct in the cat. The in vivo potential diagnostic value of the MRI study is highlighted. Cerebellar infarcts should be included in the differential diagnosis of cat with a peracute onset of cerebellar signs regardless of the severity of neurological deficits.
Lafora disease is a fatal genetic disorder characterised by neurotoxic deposits of malformed insoluble glycogen. In humans it is caused by mutation in the EPM2A or NHLRC1 genes. There is a known mutation in miniature wirehaired dachshunds which has not been documented in other dog breeds, including beagles, in which the disease is relatively commonly reported. This case report describes the causative defect in two affected beagles, namely the same massive expansion as in miniature wirehaired dachshunds of a 12-nucleotide repeat sequence that is unique to the canine NHLRC1 gene. This is the first mutation described in beagles with Lafora disease, and so far the only Lafora disease genetic variant in dogs.
Several toy breed dogs are predisposed to syringomyelia (SM), a spinal cord disorder, characterised by fluid-filled cavitation. SM is a complex trait with a moderately high heritability. Selective breeding against SM is confounded by its complex inheritance, its late onset nature and high prevalence in some breeds. This study investigated the early outcome of existing SM breeding guidelines. Six hundred and forty-three dogs, 550 Cavalier King Charles spaniels (CKCS) and 93 Griffon Bruxellois (GB), were identified as having either one (454 dogs) or both parents (189 dogs) with MRI-determined SM status. Offspring without SM were more common when the parents were both clear of SM (SM-free; CKCS 70 per cent, GB 73 per cent). Conversely, offspring with SM were more likely when both parents had SM (SM-affected; CKCS 92 per cent, GB 100 per cent). A mating of one SM-free parent with an SM-affected parent was risky for SM affectedness with 77 per cent of CKCS and 46 per cent of GB offspring being SM-affected. It is recommended that all breeding dogs from breeds susceptible to SM be MRI screened; that the SM status at five years old is established; and all results submitted to a central database that can be used by dog breeders to better enable mate selection based on estimated breeding values.
The disease complex Chiari-like malformation (CM) and syringomyelia (SM) has been associated with the development of neuropathic pain (NeP), and commonly affects Cavalier King Charles spaniels (CKCS). This prospective cohort study followed 48 CKCSs with CM and/or SM and clinical signs suggestive of NeP for a period of 39 (±14.3) months from diagnosis. At the end of the study, 36 dogs were still alive; five dogs died of an unrelated or unknown cause, and seven were euthanased due to severe clinical signs suggestive of NeP. During the follow-up period, the clinical signs of scratching, facial rubbing behaviour, vocalisation and exercise ability were evaluated. Nine out of 48 dogs stopped scratching (P
A resource was created for a third-year Neurology module using the Xerte Bootstrap template. Students were given 3 hours to work through cases and log answers in an online survey, then 1 hour for a wrap-up session where group answers were discussed then answers revealed. This format proved overwhelmingly positive for students.
OBJECTIVE: To compare radiographic morphology of the atlantoaxial region between Cavalier King Charles Spaniels (CKCSs) and dogs of other breeds and determine whether there was an association between radiographic morphology of the atlantoaxial region and syringomyelia in CKCSs. ANIMALS: 65 CKCSs and 72 dogs of other breeds. PROCEDURES: The amount that the spinous process of the axis overlapped the dorsal arch of the atlas, the relative size of the spinous process of the axis, and the amount of widening of the atlantoaxial joint that occurred when the neck was moved from a neutral to a flexed position were measured on lateral radiographic projections of the atlantoaxial region. Magnetic resonance images were reviewed to identify CKCSs with syringomyelia. RESULTS: The amount of overlap of the atlas and axis and the relative size of the spinous process of the axis were significantly smaller in CKCSs than in dogs of other breeds. However, the amount of widening of the atlantoaxial joint that occurred when the neck was moved from a neutral to a flexed position was not significantly different between groups, and no association was detected between syringomyelia and excessive atlantoaxial joint space widening or between syringomyelia and an excessively small axial spinous process. CONCLUSIONS AND CLINICAL RELEVANCE: Results suggested that radiographic morphology of the atlantoaxial region in CKCSs differs from morphology of that region in dogs of other breeds, but that these differences do not account for why some CKCSs develop syringomyelia and others do not.
Syringomyelia is an increasingly common diagnosis in veterinary medicine, especially in toy breed dogs where selections for small size and brachycephalic head shape are contributing factors. The most common cause is a condition analogous to Chiari I malformation in humans. This chapter details the pathophysiology, clinical signs, medical and surgical management, progression and prognosis of the canine condition. As a naturally occurring model of both syringomyelia and central neuropathic pain, observations that may have relevance to understanding of the pathophysiology of Chiari malformation and syringomyelia in humans are discussed. Finally, current knowledge of genetic factors and breeding advice is reviewed.
Background The Chihuahua dog breed is known for frequent occurrence of a bregmatic fontanelle on the dorsal skull. A common conception is that this skull defect is a clinically irrelevant finding. No studies, however, describe its prevalence or whether it is accompanied by other persistent fontanelles (PFs). Although Chihuahuas are predisposed to Chiari-like malformation (CM) and syringomyelia (SM), it is unknown whether PFs occur more commonly in dogs with clinical signs that are caused by CM or SM. Hypothesis/Objectives To describe the number and location of PFs at cranial sutures (CSs) and to compare the occurrence of these PFs in dogs with and without CM/SM-related clinical signs. We hypothesized that PFs also occur commonly at lateral and caudal cranial surfaces, affect a higher number of CSs, and are larger in dogs with CM/SM-related clinical signs. Animals Fifty client-owned Chihuahuas with or without CM/SM-related clinical signs. Results Of the 50 dogs evaluated, 46 (92%) had either 1 or several PFs. The mean ± SD number of PFs was 2.8 ± 3.0 (range, 0-13). A total of 138 PFs occupied 118 CSs with 57 (48%) located dorsally, 44 (37%) caudally, and 17 (14%) laterally. The number of CSs affected by PFs was significantly higher (P ≤ .001) and total PF area was significantly larger (P = .003) in dogs with CM/SM-related clinical signs. Conclusions and Clinical Importance Persistent fontanelles are very common in this group of Chihuahuas and appear at dorsal, lateral, and caudal cranial surfaces. They are more numerous and larger in Chihuahuas with CM/SM-related clinical signs.
Canine idiopathic epilepsy (IE) is the most common chronic neurological brain disease in dogs, yet it can only be diagnosed by exclusion of all other potential causes. In people, epilepsy has been associated with a reduction in brain volume. The objective was to estimate the volume of the forebrain (FB), subarachnoid space (SAS) and lateral ventricles (LV) in dogs with IE compared to controls using Cavalieri's principle. MRI scans of case and control dogs were identified from two neurology referral hospital databases. Eight breeds with increased odds of having IE were included: Golden Retriever, Labrador Retriever, Cocker Spaniel, Border terrier, German Shepherd dog, Parson Jack Russell terrier, Boxer, and Border Collie. Five dogs of each breed with IE and up to five controls were systematically and uniformly randomly sampled (SURS). The volume of the FB, SAS and LV were estimated from MRI scans by one blinded observer using Cavalieri's principle. One hundred-two dogs were identified; 56 were diagnosed with IE and 46 were controls. There was no statistically significant difference in FB, SAS and LV volume between dogs with IE and controls. Dogs with a history of status epilepticus had significantly larger FB than those without (p = 0.05). There was a border-line trend for LV volume to increase with increasing length of seizure history in the IE group (p = 0.055). The volumes of the FB, SAS and LV are not different between dogs with IE and controls, so IE remains a diagnosis of exclusion with no specific neuroanatomical biomarkers identified. This is the first time FB and SAS volume has been compared in dogs with IE. Unfortunately, we have shown that the results reporting significantly larger FBs in dogs with status epilepticus and LV volume increase with length of seizure history were likely confounded by breed and should be interpreted cautiously. Whilst these associations are interesting and clinically relevant, further investigation with breed-specific or larger, breed-diverse populations are required to permit strong conclusions. The Cavalieri principle provided an effective estimation of FB, SAS and LV volumes on MRI, but may be too time-intensive for use in clinical practice.
Syringomelia is a relatively rare clinical entity in which fluid-filled cavities develop within the spinal cord. Although modern imaging technologies usually permit an accurate diagnosis at an early stage, syringomyelia remains an enigmatic condition. This reference monograph provides an up-to-date account of the present state of understanding of syringomyelia and related disorders. The editors aim to document the best clinical practice in diagnosis and treatment and to provide clear guidance on how to reduce the incidence of severe outcomes. New challenges are addressed, including the appropriate management of the increasing number of apparently idiopathic syrinx cavities that are detected. In addition, controversies in current practice and directions for future research are fully discussed. Syringomelia will be an invaluable source of information for experts in the field, specialists in various related disciplines and other interested health care professionals.
The prevalence of syringomyelia was investigated in a sample population of 555 Cavalier King Charles spaniels. All dogs, which were declared by their owners to be showing no clinical signs of syringomyelia, underwent MRI to determine the presence or absence of the condition. Data were analysed by logistic regression to determine the effects of sex and age on the prevalence of syringomyelia. Only increased age was found to have a significant effect. The prevalence of syringomyelia was 25 per cent in dogs aged 12 months, increasing to a peak of 70 per cent in dogs aged 72 months or more.
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate long-term success of cranial cervical decompression for management of canine Chiari-like malformation with syringomyelia (CM/SM). STUDY DESIGN: Retrospective clinical study. ANIMALS: Cavalier King Charles spaniels (n=15). METHODS: After diagnosis by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) dogs had cranial cervical decompression with durotomy. Seven dogs had the durotomy patched with biocompatible collagen matrix. Clinical outcome was monitored for >12 months. RESULTS: All dogs either improved (80%) or were unchanged (20%) postoperatively. Postoperative MRI in 6 dogs revealed persistence of syringomyelia. Seven dogs (47%) subsequently deteriorated, 0.2-2.3 years after surgery (mean, 1.3 years) and 2 dogs were eventually euthanatized as a consequence. Twelve dogs were still alive, 1-6.5 years after surgery (mean, 2.5 years). CONCLUSION: Cranial cervical decompression surgery is associated with low mortality and morbidity, and results in clinical improvement in most dogs. The procedure seemingly does not result in syrinx collapse and resolution. Clinical improvement may not be sustained and some dogs can be expected to deteriorate. CLINICAL RELEVANCE: Cranial cervical decompression surgery may have a role in management of CM/SM. In dogs with severe pain, it can improve quality of life for several years; however, it does not appear to adequately address the primary cause of syringomyelia. Further prospective study is needed to better understand the pathogenesis and treatment of this disorder. Because this condition causes neuropathic pain but does not necessarily result in euthanasia more information is needed on appropriate pain management for these patients.
Covid-19 lockdowns dramatically accelerated demand for companion family animals. But increased selective breeding of flat-faced dogs has led to a crisis in associated neurological, skeletal, and airway disorders, where canine quality of life is inadvertently sacrificed for cuteness in appearance. It is suggested that some physical traits are more likely to be found in pedigree dogs afflicted with several genetic developmental disorders, and the exaggeration of these traits worsen the severity of such disorders. However, identifying and grading these traits is impractical without large-scale medical imaging and invasive surgical procedures. A database comprising CT scans obtained from Cavalier King Charles Spaniels was provided to this study, from which cranial models can be generated with computer vision software. A novel low-cost AI methodology has been developed to identify key physical characteristics, present in crania, associated with genetic developmental diseases affecting the Cavalier. Early AI-led results found a significant bulge on the top of the skull linked to neurological disease with near-perfect sensitivity. Continuing developments of this methodology will assist breeders to better develop sustainable, ethical breeding practices for at-risk pedigree dogs and contribute to reducing quality of life issues arising from genetic developmental disorders.
Background: A retrospective case series study was undertaken to describe the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)findings in Pug dogs with thoracolumbar myelopathy and concurrent caudal articular process (CAP) dysplasia. Electronic clinical records were searched for Pug dogs who underwent MRI for the investigation of a T3-L3 spinalcord segment disease with subsequent confirmation of CAP dysplasia with computed tomography between January 2013 and June 2017. Clinical parameters age, gender, neuter status, body weight, urinary or faecal incontinence, severity and duration of clinical signs were recorded. MRI abnormalities were described. Univariablenon-parametric tests investigated the association between the clinical parameters and evidence of extra- or intra-dural spinal cord compression on MRI. Results: 18 Pug dogs were included. The median age was 106 months with median duration of clinical signs 5months. All presented with variable severity of spastic paraparesis and ataxia; 50% suffered urinary/faecalincontinence. In all cases, MRI revealed a focal increase in T2-weighted signal intensity within the spinal cord at anintervertebral level where bilateral CAP dysplasia was present; this was bilateral aplasia in all but one case, whichhad one aplastic and one severely hypoplastic CAP. MRI lesions were associated with spinal cord compression in allbut one case; intervertebral disc protrusion resulted in extra-dural compression in 10 (56%) cases; intra-duralcompression was associated with a suspected arachnoid diverticulum in 4 (22%) cases and suspected pia-arachnoidfibrosis in 3 cases (17%). There was no association between clinical parameters and a diagnosis of intra-dural vsextra-dural compression. CAP dysplasia occurred at multiple levels in the T10–13 region with bilateral aplasia atT11–12 most often associated with corresponding spinal cord lesions on MRI. Conclusions: All Pugs dogs in this study were presented for chronic progressive ambulatory paraparesis;incontinence was commonly reported. Although intervertebral disc disease was the most common radiologic diagnosis, intra-dural compression associated with arachnoid diverticulae/fibrosis was also common. Bilateral CAPaplasia was present in all but one Pug dog at the level of MRI detectable spinal cord lesions. A causal relationship between CAP dysplasia and causes of thoracolumbar myelopathy is speculated but is not confirmed by this study.
Psychiatric comorbidities affect a large percentage of people with epilepsy and have a detrimental impact on their quality of life. Recently, behavioural comorbidities, with similar characteristics to human psychiatric diseases, have been identified in dogs with idiopathic epilepsy. In particular, behaviours motivated by the fear–anxiety emotional system have been found to be associated with the occurrence of idiopathic epilepsy in both dogs receiving anti-epileptic drugs, and drug-naïve dogs. There has been little research into the relationship between epilepsy and behavioural signs, and even less into potential treatment protocols. The following article will review available literature from human medicine to describe the current state of knowledge about the bi-directional relationship between anxiety and epilepsy, draw parallels from reported anxiogenic and anxiolytic properties of anti-epileptic drugs and attempt to provide pharmaceutical and behavioural guidance for veterinary patients with epilepsy and comorbid anxiety.
The amyloidoses constitute a group of diseases occurring in humans and animals that are characterized by abnormal deposits of aggregated proteins in organs, affecting their structure and function. In the Abyssinian cat breed, a familial form of renal amyloidosis has been described. In this study, multi-omics analyses were applied and integrated to explore some aspects of the unknown pathogenetic processes in cats. Whole-genome sequences of two affected Abyssinians and 195 controls of other breeds (part of the 99 Lives initiative) were screened to prioritize potential disease-associated variants. Proteome and miRNAome from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded kidney specimens of fully necropsied Abyssinian cats, three affected and three non-amyloidosis-affected were characterized. While the trigger of the disorder remains unclear, overall, (i) 35,960 genomic variants were detected; (ii) 215 and 56 proteins were identified as exclusive or overexpressed in the affected and control kidneys, respectively; (iii) 60 miRNAs were differentially expressed, 20 of which are newly described. With omics data integration, the general conclusions are: (i) the familial amyloid renal form in Abyssinians is not a simple monogenic trait; (ii) amyloid deposition is not triggered by mutated amyloidogenic proteins but is a mix of proteins codified by wild-type genes; (iii) the form is biochemically classifiable as AA amyloidosis.
This article, which is based on the PhD thesis of Clare Rusbridge, is a review of chiari-like malformation and syringomyelia in the Cavalier King Charles Spaniel. The abnormality is becoming more common among dwarf breeds and brachychepalic breeds. The nature, prevalence, and treatment of the disease are described, as is current knowledge on its heritability in the Cavalier King Charles Spaniel.
Lafora disease (LD) is an autosomal recessive late onset, progressive myoclonic epilepsy with a high prevalence in the miniature Wirehaired Dachshund. The disease is due to a mutation in the Epm2b gene which results in intracellular accumulation of abnormal glycogen (Lafora bodies). Recent breed-wide testing suggests that the carrier plus affected rate may be as high as 20%. A characteristic feature of the disease is spontaneous and reflex myoclonus; however clinical signs and disease progression are not well described. A survey was submitted to owners of MWHD which were homozygous for Epm2b mutation (breed club testing program) or had late onset reflex myoclonus and clinical diagnosis of LD. There were 27 dogs (11 male; 16 female) for analysis after young mutation-positive dogs that had yet to develop disease were excluded. Average age of onset of clinical signs was 6.94 years (3.5–12). The most common initial presenting sign was reflex and spontaneous myoclonus (77.8%). Other presenting signs included hypnic myoclonus (51.9%) and generalized seizures (40.7%). Less common presenting signs include focal seizures, “jaw smacking”, “fly catching”, “panic attacks”, impaired vision, aggression and urinary incontinence. All these clinical signs may appear, and then increase in frequency and intensity over time. The myoclonus in particular becomes more severe and more refractory to treatment. Signs that developed later in the disease include dementia (51.9%), blindness (48.1%), aggression to people (25.9%) and dogs (33.3%), deafness (29.6%) and fecal (29.6%) and urinary (37.0%) incontinence as a result of loss of house training (disinhibited type behavior). Further prospective study is needed to further characterize the canine disease and to allow more specific therapeutic strategies and to tailor therapy as the disease progresses.
We report persistence of associated syringomyelia and formation of newly caudal spinal arachnoid diverticulum, following marsupialization surgery. We describe syringopleural shunt placement as a novel approach to treat both conditions in a Pug dog.
Chiari-like malformation (CM)/syringomyelia (SM) is a disease complex recognised in Cavalier King Charles spaniels (CKCSs) that can lead to neuropathic pain (NeP). In humans, NeP is associated with anxiety, depression and reduced quality of life (QoL). In this study, databases of three specialist veterinary centres were searched and CKCS breed societies and health forums were contacted to identify CKCS with an imaging diagnosis of CM/SM. Owners completed questionnaires on behaviour, signalment, general health status, NeP and QoL. Data were analysed from 122 dogs out of 564 questionnaires completed, after incomplete questionnaires and data from dogs that had other potentially debilitating disease processes were excluded. NeP severity score was significantly and positively correlated with 'stranger-directed' fear (r(S)=0.28), non-social fear (r(S)=0.34), 'separation-related' behaviour (r(S)=0.38), attachment behaviour (r(S)=0.24), excitability (r(S)=0.21) and proxy for pain sensation (r(S)=0.29). Increased NeP was also significantly associated with decreased QoL (r(S)=0.47), ability to settle (r(S)=0.26) and willingness to exercise (r(S)=0.50). Severity of NeP was positively associated with certain fear-associated behaviour and with decreased owner-perceived QoL. Thus, neurobehavioural changes should be considered in the management of NeP in CKCS with CM/SM.
OBJECTIVES: This study describes Chiari-like malformation and syringomyelia in the Griffon Bruxellois and establishes if skull radiographs are useful for disease prediction. METHODS: Magnetic resonance imaging from 56 Griffon Bruxellois dogs was assessed for Chiari-like malformation and cerebrospinal fluid pathway abnormalities. Skull radiographs were obtained in 33 dogs. Two rostrocaudal and two ventrodorsal measurements were made, and ratios of one length to another were compared. RESULTS: In this selected sample, 60.7 per cent had Chiari-like malformation. Syringomyelia occurred with and without Chiari-like malformation (37.5 and 8.9 per cent study population, respectively). The radiographic study demonstrated that one measurement ratio could be used to predict Chiari-like malformation (sensitivity of 87 per cent and specificity of 78 per cent) and that there were significant interaction factors between sex and syringomyelia for two measurement ratios. CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE: The study suggests that Chiari-like malformation is characterised by a shortening of the basicranium and supra-occipital bone with a compensatory lengthening of the cranial vault, especially the parietal bone. We described a simple radiographic technique, which may be useful as a screening test until a more definite genetic test for Chiari-like malformation is available.
OBJECTIVES: To assess if the volumes of the caudal cranial fossa (CCF), parenchyma within the caudal cranial fossa (CCFP) or ventricles (V) are associated with syringomyelia (SM) in cavalier King Charles spaniels (CKCS) with Chiari-like malformation (CM). To evaluate if volumes are associated with transverse syrinx width. METHODS: Magnetic resonance images of 59 CKCS with CM were retrospectively reviewed and grouped with or without SM. Three-dimensional images were created and volumes of the fossae, brain parenchyma and ventricular system were calculated from which percentages of CCF, CCFP and V were created. If present, syrinx size was measured from its maximal transverse width. The percentages were statistically compared between groups, and correlation between percentages and syrinx dimensions was made. RESULTS: CKCS with SM had significantly higher CCFP (P=0.0001) and V (P=0.0002) to those without but no significant difference in CCF (P=0.925). There was a positive correlation between CCFP and syrinx width (Pearson r=0.437) and ventricle size to syrinx width (Spearman r=0.627). CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE: A more marked overcrowding of the CCF is associated with SM, which may explain the high incidence of SM in CKCS with CM. The association between ventricle and syrinx dimensions supports the theory that SM development is the result of altered cerebrospinal fluid dynamics.
This was a retrospective study on the clinical features and response to treatment in seven cats with feline hyperaesthesia syndrome (FHS) and tail mutilation. FHS is a poorly understood disorder characterised by skin rippling over the dorsal lumbar area, episodes of jumping and running, excessive vocalisation, and tail chasing and self-trauma. The majority of the cats were young, with a median age of 1 year at the onset of clinical signs, male (n = 6) and with access to the outdoors (n = 5). Multiple daily episodes of tail chasing and self-trauma were reported in five cats, with tail mutilation in four cats. Vocalisation during the episodes (n = 5) and rippling of lumbar skin (n = 5) were also reported. Haematology, serum biochemistry, Toxoplasma gondii and feline immunodeficiency virus/feline leukaemia virus serology, MRI scans of brain, spinal cord and cauda equina, cerebrospinal fluid analysis and electrodiagnostic tests did not reveal any clinically significant abnormalities. A definitive final diagnosis was not reached in any of the cats, but hypersensitivity dermatitis was suspected in two cases. A variety of medications was used alone or in combination, including gabapentin (n = 6), meloxicam (n = 4) antibiotics (n = 4), phenobarbital (n = 2), prednisolone (n = 2) and topiramate (n = 2); ciclosporin, clomipramine, fluoxetine, amitriptyline and tramadol were used in one cat each. Clinical improvement was achieved in six cases; in five cats complete remission of clinical signs was achieved with gabapentin alone (n = 2), a combination of gabapentin/ciclosporin/amitriptyline (n = 1), gabapentin/prednisolone/phenobarbital (n = 1) or gabapentin/topiramate/meloxicam (n = 1).
Background: In dogs with ischaemic stroke, a very common site of infarction is the cerebellum. The aim of this study was to characterise neurological signs in relation to infarct topography in dogs with suspected cerebellar ischaemic stroke and to report short-term outcome confined to the hospitalisation period. A retrospective multicentre study of dogs with suspected cerebellar ischaemic stroke examined from 2010–2015 at five veterinary referral hospitals was performed. Findings from clinical, neurological, and paraclinical investigations including magnetic resonance imaging were assessed. Results: Twenty-three dogs, 13 females and 10 males with a median age of 8 years and 8 months, were included in the study. The Cavalier King Charles Spaniel (n = 9) was a commonly represented breed. All ischaemic strokes were located to the vascular territory of the rostral cerebellar artery including four extensive and 19 limited occlusions. The most prominent neurological deficits were gait abnormalities (ataxia with hypermetria n = 11, ataxia without hypermetria n = 4, non-ambulatory n = 6), head tilt (n = 13), nystagmus (n = 8), decreased menace response (n = 7), postural reaction deficits (n = 7), and proprioceptive deficits (n = 5). Neurological signs appeared irrespective of the infarct being classified as extensive or limited. All dogs survived and were discharged within 1–10 days of hospitalisation. Conclusions: Dogs affected by rostral cerebellar ischaemic stroke typically present with a collection of neurological deficits characterised by ataxia, head tilt, and nystagmus irrespective of the specific cerebellar infarct topography. In dogs with peracute to acute onset of these neurological deficits, cerebellar ischaemic stroke should be considered an important differential diagnosis, and neuroimaging investigations are indicated. Although dogs are often severely compromised at presentation, short-term prognosis is excellent and rapid clinical improvement may be observed within the first week following the ischaemic stroke.
Background A classic sign of canine syringomyelia (SM) is scratching towards one shoulder. Using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) we investigate the spinal cord lesion relating to this phenomenon which has characteristics similar to fictive scratch secondary to spinal cord transection. Medical records were searched for Cavalier King Charles spaniels with a clinical and MRI diagnosis of symptomatic SM associated with Chiari-like malformation (CM). The cohort was divided into SM with phantom scratching (19 dogs) and SM but no phantom scratching (18 dogs). MRI files were anonymised, randomised and viewed in EFILM ™. For each transverse image, the maximum perpendicular dimensions of the syrinx in the dorsal spinal cord quadrants were determined. Visual assessment was made as to whether the syrinx extended to the superficial dorsal horn (SDH). Results We showed that phantom scratching appears associated with a large dorsolateral syrinx that extends to the SDH in the C3-C6 spinal cord segments (corresponding to C2-C5 vertebrae). Estimated dorsal quadrant syrinx sizes based on the perpendicular diameters were between 2.5 and 9.5 times larger in dogs with phantom scratching, with the largest mean difference p-value being 0.009. Conclusion SM associated phantom scratching appears associated with MRI findings of a large syrinx extending into the mid cervical SDH. We hypothesise that damage in this region might influence the lumbosacral scratching central pattern generator (CPG). If a scratching SM affected dog does not have a large dorsolateral cervical syrinx with SDH involvement then alternative explanations for scratching should be investigated.
BACKGROUND: Syringomyelia (SM) is a painful neurological condition, prevalent in brachycephalic toy breeds including the Cavalier King Charles Spaniel (CKCS). In these breeds, SM is typically secondary to Chiari-like Malformation (CM). There has been much debate in the scientific and veterinary communities to what extent head shape is indicative of either pathology, especially as certain craniosynostosis syndromes in humans (highly associated with CM) have characteristic facial and cranial morphologies. Elucidating a risk morphology would allow for selection away from these traits and proffer further breeding guidelines for the condition. Dogs were measured in multiple countries by means of a standardised bony landmark measuring protocol and photo analysis by blinded, trained researchers. RESULTS: The results found two significant risk factors in the conformation of the CKCS: extent of brachycephaly and distribution of cranium. The study identified a greater amount of cranium distributed caudally (relative to the amount distributed rostrally) to be significantly protective against syrinx development at the levels of three years of age, five years of age and when comparing a sample of SM clear individuals over the age of five to those affected younger than three years of age. A decreased cephalic index (decreasing brachycephaly) was significantly protective at the latter level. Cephalic index and caudal cranium distribution exhibited a negative, linear relationship. Cephalic index demonstrated a positive linear relationship with the amount of doming of the head. CONCLUSIONS: This study proposes a risk phenotype of brachycephaly with resulting rostrocaudal doming that is more rostrally distributed and hence sloping caudally. The results of this study may allow for selection against risk aspects of conformation in the CKCS in combination with the British Veterinary Association/Kennel Club CM/SM scheme to enable reduction in CM/SM incidence. Further research comparing this external risk phenotype to the internal presentation upon MRI would determine how these features are indicative of syrinx development. Utilising breeds in which CM free individuals are more available may allow for validation of this risk phenotype for CM or determine alternatives.
Brachycephalic dogs remain popular, despite the knowledge that this head conformation is associated with health problems, including airway compromise, ocular disorders, neurological disease, and other co-morbidities. There is increasing evidence that brachycephaly disrupts cerebrospinal fluid movement and absorption, predisposing ventriculomegaly, hydrocephalus, quadrigeminal cistern expansion, Chiari-like malformation, and syringomyelia. In this review, we focus on cerebrospinal fluid physiology and how this is impacted by brachycephaly, airorhynchy, and associated craniosynostosis.
Background Occipitoatlantoaxial malformation (OAAM) is reported rarely in dogs and few treatment options are described. The congenital condition is thought to be associated with a proatlas re-segmentation failure resulting in malformation and malalignment of the craniovertebral junction which can result in C1 to 5 myelopathic signs. Methods Customized three-dimensional printed locking plate with trajectory screw implantation points for the stabilization of the atlantoaxial joint in a dog with OAAM. The dog was evaluated at time points 0, 2, 6 and 9 months to determine clinical outcome, degree of fusion, implant positioning and subsidence. Results New bone formation was noted 9 months after surgery, but complete fusion remained absent, although no implant failure occurred. Clinically, the dog made a good recovery and was able to exercise normally 9 months after surgery. The only residual deficit was a subtle left-sided cervical torticollis. Clinical Significance This report illustrates a management option and outcome of a dog treated with OAAM. Collaboration between clinicians and engineers provides a new dimension of care for patients with vertebral malformations.
Background A retrospective study of the clinicopathological features of presumed and confirmed cases of idiopathic inflammatory polymyopathy in the Hungarian Vizsla dog and guidelines for breeding. Results 369 medical records were reviewed (1992–2013) and 77 Hungarian Vizslas were identified with a case history consistent with idiopathic inflammatory polymyopathy. Inclusion criteria were: group 1 (confirmed diagnosis); histopathology and clinical findings compatible with an inflammatory polymyopathy and group 2 (probable diagnosis); clinical findings compatible with a polymyopathy including dysphagia, sialorrhea, temporal muscle atrophy, elevated serum creatine kinase (CK) activity, and sufficient clinical history to suggest that other neuromuscular disorders could be ruled out. Some group 2 dogs had muscle biopsy, which suggested muscle disease but did not reveal an inflammatory process. The mean age of onset was 2.4 years; male dogs were slightly overrepresented. Common presenting signs were dysphagia, sialorrhea, masticatory muscle atrophy, and regurgitation. Common muscle histopathological findings included degenerative and regenerative changes, with multifocal mononuclear cell infiltration with lymphoplasmacytic myositis of variable severity. A positive response to immunosuppressive treatment supported an immune-mediated aetiology. The mean age at death and survival time were 6.4 and 3.9 years, respectively. Recurrence of clinical signs and aspiration pneumonia were common reasons for euthanasia. Conclusions Diagnosis of Vizsla idiopathic inflammatory polymyopathy can be challenging due to lack of specific tests, however the presence of dysphagia, regurgitation and masticatory muscle atrophy in this breed with negative serological tests for masticatory muscle myositis and myasthenia gravis, along with muscle biopsies suggesting an inflammatory process, support the diagnosis. However, there is an urgent need for a more specific diagnostic test. The average of inbreeding coefficient (CoI) of 16.3% suggests an increased expression of a Dog Leukocyte Antigen Class II haplotype, leading to an increased disease risk. The prognosis remains guarded, as treatment can only manage the disease. Recurrence of clinical signs and perceived poor quality of life are the most common reasons for humane euthanasia.
Background: Chiari-like malformation (CM) is a complex malformation of the skull and cranial cervical vertebrae potentially resulting in pain and secondary syringomyelia (SM). CM associated pain can be challenging to diagnose [35]. We propose a machine learning approach to characterize morphological changes in dogs that may/may not be apparent to human observers. This data driven approach can remove potential bias (or blindness) that may be produced by a hypothesis driven expert observer approach. Hypothesis/Objectives: Using a novel machine learning approach to understand neuromorphological change and to identify image-based biomarkers in dogs with CM associated pain (CM-P) and symptomatic SM (SM-S), with the aim of deepening the understanding on these disorders. Animals: 32 client owned Cavalier King Charles Spaniels (CKCS) (11 controls, 10 CM-P, 11 SM-S) Methods: Retrospective study using T2W midsagittal DICOM anonymized images which were mapped to a images of a average clinically normal CKCS reference using Demons image registration. Key deformation features were automatically selected from the resulting deformation maps. A kernelized Support Vector Machine was used for classifying characteristic localized changes in morphology. Results: Candidate biomarkers were identified with receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves with area under the curve (AUC) of 0.78 (sensitivity = 82%; specificity = 69%) for the CM-P biomarkers collectively, and an AUC of 0.82 (sensitivity = 93%; specificity = 67%) for the SM biomarkers collectively. Conclusions and clinical importance: Machine learning techniques can assist CM/SM diagnosis and understand abnormal morphology location with the potential to be applied to a variety of breeds and conformational diseases.
Dogs exhibit a range of immune-mediated conditions including a lymphocytic thyroiditis which has many similarities to Hashimoto's thyroiditis in man. We have recently reported an association in Doberman Pinschers between canine hypothyroidism and a rare DLA class II haplotype that contains the DLA-DQA1*00101 allele. We now report a further series of 173 hypothyroid dogs in a range of breeds where a significant association with DLA-DQA1*00101 is shown.
Background: Advances in mobile technology mean vets are now commonly presented with videos of paroxysmal events by clients, but the consistency of the interpretation of these videos has not been investigated. The objective of this study was to investigate the level of agreement between vets (both neurology specialists and non-specialists) on the description and classification of videos depicting paroxysmal events, without knowing any results of diagnostic workup. An online questionnaire study was conducted, where participants watched 100 videos of dogs and cats exhibiting paroxysmal events and answered questions regarding: epileptic seizure presence (yes/no), seizure type, consciousness status, and the presence of motor, autonomic and neurobehavioural signs. Agreement statistics (percentage agreement and kappa) calculated for each variable, with prevalence indices calculated to aid their interpretation. Results: Only a fair level of agreement (κ = 0.40) was found for epileptic seizure presence. Overall agreement of seizure type was moderate (κ = 0.44), with primary generalised seizures showing the highest level of agreement (κ = 0.60), and focal the lowest (κ =0.31). Fair agreement was found for consciousness status and the presence of autonomic signs (κ = 0.21–0.40), but poor agreement for neurobehavioral signs (κ = 0.16). Agreement for motor signs ranged from poor (κ = ≤ 0.20) to moderate (κ = 0.41–0.60). Differences between specialists and non-specialists were identified. Conclusions: The relatively low levels of agreement described here highlight the need for further discussions between neurology experts regarding classifying and describing epileptic seizures, and additional training of non-specialists to facilitate accurate diagnosis. There is a need for diagnostic tools (e.g. electroencephalogram) able to differentiate between epileptic and non-epileptic paroxysms.
The clinical and clinicopathological characteristics, treatment and outcome of vermicular muscle contractions (myokymia) and generalized muscle stiffness (neuromyotonia) in 37 Jack Russell terriers were evaluated retrospectively. Thirty dogs were affected by both disorders, whereas seven were presented with myokymia and never developed neuromyotonia. Clinical signs started at the mean age of 8 months. Except for signs of myokymia and neuromyotonia, clinical and neurological examination was normal in all dogs. Thirty dogs demonstrated typical signs of hereditary ataxia. Changes in serum chemistry included increased creatine kinase, aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase concentrations. Electromyographic abnormalities, especially in muscles showing macroscopically visible myokymia, consisted of semirhythmic bursts of doublet, triplet, or multiplet discharges of a single motor unit. The amplitudes varied between 80 μV and 1 mV and occurred with an interburst frequency between 10 and 40 Hz and an intraburst frequency between 150 and 280 Hz. Most dogs were treated with a sodium channel blocker with variable results. Seven dogs died (most likely because of hyperthermia) or were euthanased during a neuromyotonic attack; 15 dogs were euthanased due to worsening of clinical signs, or lack of or no long-lasting effect of medication, and three were euthanased for unknown or unrelated reasons. Nine dogs were lost to follow-up and three were still alive 5-10.5 years after the start of clinical signs. In conclusion, young Jack Russell terriers with myokymia and neuromyotonia should undergo a complete blood and electrophysiological examination. Long-term prognosis is not favourable.
BackgroundThere is limited published information to guide the clinical management of bacterial meningitis/encephalitis in dogs. MethodsThis was a retrospective case series comprising 10 French bulldogs from two referral centres. The cases were diagnosed with bacterial meningitis/encephalitis suspected secondary to otogenic infection based on detection of abnormal fluid/soft tissue opacity within the middle/inner ear, associated meningeal/intracranial involvement through MRI, the findings of cerebro-spinal fluid (CSF) analysis suggestive of sepsis and/or clinical improvement following antibiosis. ResultsTen dogs were included (three female and seven male), with a median age of 60 months. Dogs presented with acute onset (median 2 days), progressive history of vestibular signs and/or intra-oral or cervical pain. Five dogs had gross signs of concurrent otitis externa. Common MRI findings included material within the tympanic bulla with adjacent meningeal enhancement. Analysis of CSF documented pleocytosis in all eight dogs, intracellular bacteria seen in three with positive bacteriological culture in two dogs. One dog was euthanised following diagnosis. Nine remaining dogs received antimicrobial therapy and six underwent surgical management. Three dogs treated surgically were neurologically normal within 2 weeks and the remaining three improved. Two dogs treated medically improved and one had complete resolution reported within a 4-week follow-up period. Study limitations include its retrospective nature and small sample size with minimal longer term follow-up. ConclusionsBacterial meningitis/encephalitis in French bulldogs can require both medical and surgical treatment to achieve a favourable outcome.
The exact pathogenesis of syringomyelia is unknown. Epidural venous distention during raised intrathoracic pressure (Valsalva) may cause impulsive movement of fluid ( "slosh ") within the syrinx. Such a slosh mechanism is a proposed cause of syrinx dissection into spinal cord parenchyma resulting in craniocaudal propagation of the cavity. We sought to test the "slosh " hypothesis by epidural excitation of CSF pulse in a computer model of canine syringomyelia. Our previously developed canine syringomyelia computer model was modified to include an epidural pressure pulse. Simulations were run for: cord free of cavities; cord with small syringes at different locations; and cord with a syrinx that was progressively expanding caudally. If small syringes are present, there are peaks of stress at those locations. This effect is most pronounced at the locations at which syringes initially form. When a syrinx is expanding caudally, the peak stress is typically at the caudal end of the syrinx. However, when the syrinx reaches the lumbar region; the stress becomes moderate. The findings support the "slosh " hypothesis, suggesting that small cervical syringes may propagate caudally. However, when the syrinx is large, there is less focal stress, which may explain why a syrinx can rapidly expand but then remain unchanged in shape over years.
Case summary A rescue charity-owned 6-month-old neutered female domestic shorthair cat was presented with progressive tetraparesis, increased extensor muscle tone and signs of spinocerebellar ataxia, including hypermetria. The cat's male sibling, with similar progressive neurological signs, had been euthanased 2 months previously. An inherited metabolic disorder was suspected. Urine for determination of organic acid concentration was obtained and the cat was prescribed carnitine and taurine supplementation. The cat was euthanased 3 months later following progressive neurological signs, including ataxia, tetraparesis, tendency to fall, bilateral absent menace response and intention tremor. A selective post-mortem examination was obtained, taking samples from the brain, cervical spinal cord, tibial branch of the sciatic nerve, muscle, liver and kidneys. Organic acid analysis results received after euthanasia revealed a marked elevation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaric acid (45 mmol/mol creatine [normal range 0-2]) and isovalerylglycine (27 mmol/mol creatinine [normal range 0-2]). 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaric acid was deemed clinically relevant as it is a metabolite of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase, the enzyme involved in the final step of leucine degradation. Post-mortem examination revealed diffuse, chronic-active, severe olivoponto-(spino)-cerebellar degeneration. Relevance and novel information This is the first report of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaric aciduria in the veterinary literature and the first description of the neuropathology of this disorder in any species. 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaric aciduria in humans occurs rarely and is due to a deficiency in 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A lyase.
Background: Autoimmune mechanisms represent a novel category for causes of seizures and epilepsies in humans, and LGI1-antibody associated limbic encephalitis occurs in cats. Hypothesis/Objectives: To investigate the presence of neural antibodies in dogs with epilepsy or dyskinesia of unknown cause using human and murine assays modified for use in dogs. Animals: Fifty-eight dogs with epilepsy of unknown cause or suspected dyskinesia and 57 control dogs. Methods: Serum and CSF samples were collected prospectively as part of the diagnostic work-up. Clinical data including onset and seizure/episode type were retrieved from the medical records. Screening for neural antibodies was done with cell-based assays transfected with human genes for typical autoimmune encephalitis antigens and tissue-based immunofluorescence assays on mouse hippocampus slices in serum and CSF samples from affected dogs and controls. The commercial human und murine assays were modified with canine-specific secondary antibody. Positive controls were from human samples. Results: The commercial assays used in this study did not provide unequivocal evidence for presence of neural antibodies in dogs including one dog with histopathologically proven limbic encephalitis. Low titer IgLON5 antibodies were present in serum from one dog from the epilepsy/dyskinesia group and in one dog from the control group. Conclusion and Clinical Importance: Specific neural antibodies were not detected using mouse and human target antigens in dogs with epilepsy and dyskinesia of unknown origin. These findings emphasize the need for canine-specific assays and the importance of control groups.
A variety of cat breeds have been developed via novelty selection on aesthetic, dermatological traits, such as coat colors and fur types. A recently developed breed, the lykoi (a.k.a. werewolf cat), was bred from cats with a sparse hair coat with roaning, implying full color and all white hairs. The lykoi phenotype is a form of hypotrichia, presenting as a significant reduction in the average numbers of follicles per hair follicle group as compared to domestic shorthair cats, a mild to severe perifollicular to mural lymphocytic infiltration in 77% of observed hair follicle groups, and the follicles are often miniaturized, dilated, and dysplastic. Whole genome sequencing was conducted on a single lykoi cat that was a cross between two independently ascertained lineages. Comparison to the 99 Lives dataset of 194 non-lykoi cats suggested two variants in the cat homolog forHairless(HR) (HRlysine demethylase and nuclear receptor corepressor) as candidate causal gene variants. The lykoi cat was a compound heterozygote for two loss of function variants inHR, an exon 3 c.1255_1256dupGT (chrB1:36040783), which should produce a stop codon at amino acid 420 (p.Gln420Serfs*100) and, an exon 18 c.3389insGACA (chrB1:36051555), which should produce a stop codon at amino acid position 1130 (p.Ser1130Argfs*29). Ascertainment of 14 additional cats from founder lineages from Canada, France and different areas of the USA identified four additional loss of functionHRvariants likely causing the highly similar phenotypic hair coat across the diverse cats. The novel variants inHRfor cat hypotrichia can now be established between minor differences in the phenotypic presentations.
Background: Diagnosis of Chiari-like malformation-associated pain (CM-P) or clinicallyrelevant syringomyelia (SM) is challenging. We sought to determine common signs.Animals:One hundred thirty client-owned Cavalier King Charles spaniels with neuroaxismagnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and diagnosis of CM-P/SM. Dogs with comorbiditiescausing similar signs were excluded with exception of otitis media with effusion (OME). Methods: Retrospective study of medical records relating signalment, signs, and MRIfindings. Dogs were grouped by SM maximum transverse diameter (1 = no SM;2 = 0.5-1.99 mm; 3 = 2-3.9 mm: 4 =≥4 mm). Differences between all groups—groups1 versus 2-4 and groups 1-3 versus 4—were investigated. Continuous variables wereanalyzed using 2-samplet-tests and analysis of variance. Associations between categori-cal variables were analyzed using Fisher's exact or chi-square tests. Results:Common signs were vocalization (65.4%), spinal pain (54.6%), reduced activ-ity (37.7%), reduced stairs/jumping ability (35.4%), touch aversion (30.0%), alteredemotional state (28.5%), and sleep disturbance (22%). Head scratching/rubbing(28.5%) was inversely associated with syrinx size (P= .005), less common in group4(P= .003), and not associated with OME (P= .977). Phantom scratching, scoliosis,weakness, and postural deficits were only seen in group 4 (SM≥4 mm;P= .004). Conclusions and Clinical Importance: Signs of pain are common in CM/SM but arenot SM-dependent, suggesting (not proving) CM-P causality. Wide (≥4 mm) SM isassociated with signs of myelopathy and, if the dorsal horn is involved, phantomscratching (ipsilateral) and torticollis (shoulder deviated ipsilateral; head tiltcontralateral).
The corticolimbic system (Fig. 1) integrates emotion with cognition and produces a behavioral output that must be flexible based on the environmental circumstances.1 The corticolimbic system circuitry of the prefrontal cortex, amygdala, and hippocampus is connected to the hypopituitary-pituitary axis, and environmental circumstances such as stress and anxiety input decision making, emotion regulation, and memory.1 The corticolimbic system is also the modulator for acute pain, a mediator for chronic pain, and critical for the chronification of pain.2 There is a high comorbidity of negative affective disorders with chronic pain and vice versa, hypothesized because of similar changes in neuroplasticity and overlapping neurobiological mechanisms.3 This article discusses 3 feline disorders that affect or are affected by the corticolimbic systems: the maladaptive pain disorder feline orofacial pain syndrome (FOPS) in which disease expression is influenced by environmental stress; feline hyperesthesia syndrome (FHS) in which there is still debate as to whether this is a primary neurobehavioral disorder or a behavioral response to a negative affective state; and limbic encephalitis, an autoimmune encephalitis that results in neurobehavioral signs and seizures. There is a focus on diagnosis and management, which is challenging in all 3 diseases.
Background Persistent fontanelles (PFs) are, in Chihuahuas, almost ubiquitous. Furthermore, Chihuahuas are predisposed to other craniomorphological abnormalities, including syringomyelia (SM), ventriculomegaly, and craniocervical junction (CCJ) overcrowding resulting in neural tissue deviation. It is, however, undetermined if PFs are more common in dogs with these structural abnormalities, and their etiology is unknown. Hypothesis/Objectives Persistent fontanelles are more numerous and larger in Chihuahuas with low body weight, older age, SM, dilated fourth ventricle, ventriculomegaly, and CCJ overcrowding. Animals Fifty client-owned Chihuahuas. Methods Cross-sectional study evaluating the association of both the number of cranial sutures affected by PFs (NAS) and total fontanelle area (TFA), based on computed tomography with SM, fourth ventricle dilatation, lateral ventricle volume, and extent of neural tissue compression at the CCJ based on magnetic resonance images. Results The NASs was higher and TFA larger in dogs with low body weight (NAS: P = .007; 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.384-0.861; TFA: P = .002; 95% CI = −1.91 to −0.478), larger lateral ventricles (NAS: P ≤ .001; 95% CI = 1.04-1.15; TFA: P ≤ .001; 95% CI = 0.099-0.363), and more severe neural tissue compression at the CCJ (NAS: P ≤ .001; 95% CI = 1.26-2.06; TFA: P = .03; 95% CI = 0.066-1.13). Similarly, dogs with SM (NAS: P = .004; 95% CI = 1.26-3.32; TFA: mean ± SD, 130 ± 217 mm2; P = .05) had higher NAS and larger TFA than did dogs without SM (43.7 ± 61.0 mm2). Age was not associated with NAS (P = .81; 95% CI = 0.989-1.01) or TFA (P = .33; 95% CI = −0.269 to 0.092). Conclusions and Clinical Importance Persistent fontanelles are associated with small size, SM, ventriculomegaly, and CCJ overcrowding.
Syringomyelia (SM) is a prevalent inherited developmental condition in Cavalier King Charles Spaniels (CKCSs) with Chiari-like malformation (CM), accompanied by a variety of clinical manifestations, including signs of neuropathic pain. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the gold standard in SM diagnosis. However, it is desirable to establish clinical predictors that can identify CKCSs with a large clinical syrinx that needs treatment, as some owners cannot afford or lack access to MRI. The aims of the study were to investigate owner-reported clinical signs of SM and clinical predictors of a large clinical syrinx, using predictive values of significant signs, individually and in combinations. Eighty-nine CKCSs participated in this retrospective study. Based on MRI diagnosis, dogs were distributed into three groups: CM without syrinx or with a maximum transverse width < 2 mm (n = 13), CM with small syrinx 2.00-3.99 mm (n = 26) and CM with large syrinx ≥4 mm (n = 50). A structured investigator-owner interview using a standardized questionnaire was used to collect data regarding clinical signs of CM and SM. The statistical tests Pearson's chi-square, Fisher's Exact and Spearman's rank order were used to assess the difference in owner-reported signs between groups. For signs with significant differences, positive and negative predictive values (PPV and NPV) were calculated. Following clinical signs were reported significantly more frequent in dogs with a large syrinx: phantom scratching, bilateral scratching of the neck or shoulder, aversion when that area is touched, or exacerbation of clinical signs when the dog is emotionally aroused. Each individual sign had a high PPV, indicative of a large clinical syrinx. The PPV increased further when the signs phantom scratching, aversion to touch to the head, neck or shoulder, and a preferred head posture during sleep were present in combination. Specific clinical signs can be used individually and in combination as clinical predictors of a large clinical syrinx in CKCSs with CM and SM. General practitioners can utilize this information to identify CKCSs with a large syrinx to initiate necessary treatment. This is particularly useful in cases where access to or affordability of an MRI diagnosis is limited.
Background: Syringomyelia is a pathological condition in which fluid-filled cavities (syringes) form and expand in the spinal cord. Syringomyelia is often linked with obstruction of the craniocervical junction and a Chiari malformation,which is similar in both humans and animals. Some brachycephalic toy breed dogs such as Cavalier King Charles Spaniels (CKCS) are particularly predisposed. The exact mechanism of the formation of syringomyelia is undetermined and consequently with the lack of clinical explanation, engineers and mathematicians have resorted to computer models to identify possible physical mechanisms that can lead to syringes. We developed a computer model of the spinal cavity of a CKCS suffering from a large syrinx. The model was excited at the cranial end to simulate the movement of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and the spinal cord due to the shift of blood volume in the cranium related to the cardiac cycle. To simulate the normal condition,the movement was prescribed to the CSF. To simulate the pathological condition, the movement of CSF was blocked. Results: For normal conditions the pressure in the SAS was approximately 400 Pa and the same applied to all stress components in the spinal cord. The stress was uniformly distributed along the length of the spinal cord.When the blockage between the cranial and spinal CSF spaces forced the cord to move with the cardiac cycle,shear and axial normal stresses in the cord increased significantly. The sites where the elevated stress was most pronounced coincided with the axial locations where the syringes typically form, but they were at the perimeter rather than in the central portion of the cord. This elevated stress originated from the bending of the cord at the locations where its curvature was high. Conclusions: The results suggest that it is possible that repetitive stressing of the spinal cord caused by its exaggerated movement could be a cause for the formation of initial syringes. Further consideration of factors such as cord tethering and the difference in mechanical properties of white and grey matter is needed to fully explore this possibility.
Background: Recent studies including an innovative machine learning technique indicated Chiari-like malformation (CM) is influenced by brachycephalic features. Objectives: Morphometric analysis of facial anatomy and dysmorphia in CM-associated pain (CM-P) and syringomyelia (SM) in the Cavalier King Charles Spaniel (CKCS). Animals:Sixty-six client-owned CKCS. Methods:Retrospective study of anonymized T2W sagittal magnetic resonance imaging of 3 clinical groups: (1) 11 without central canal dilation (ccd) or SM (CM-N),(2) 15 with CM-P with no SM or
Many epileptic patients will have satisfactory seizure control using the first-line anticonvulsants phenobarbital and/or bromide, as discussed in the first article of this series (In Practice, March 2013, vol 35, pp 106-113). However, some patients will continue to have an unacceptable number or severity of seizures despite adequate drug serum concentrations. Some patients have a compromised quality of life because of the adverse effects of their medication. In this article, the anticonvulsant drugs used for second-line therapy are discussed, together with other anticonvulsants and alternative therapies.
Background: Chiari-like malformation (CM) is a developmental condition, characterised by a conformational change and overcrowding of the brain and cranial cervical spinal cord. CM-associated pain (CM-P) and syringomyelia are increasingly being diagnosed, due to the rising popularity of predisposed brachycephalic breeds and the availability of MRI in veterinary practices.
This case report documents two pathological variations of potentially inherited, cerebellar cortical abiotrophy in two unrelated Lagotto Romagnolo breed dogs. The first dog had an atypical lesion in the cerebellar cortex with depletion of cerebellar granular cell layer and sparing of the Purkinje cell layer. The second case had degenerative changes in both Purkinje and granular cell layers. The clinical picture was similar in both cases presented, although the severity of the signs of cerebellar dysfunction varied.
This article aims to give the general practitioner a step by step approach to first-line medical management of epilepsy in both cats and dogs. The licensed drugs, bromide and phenobarbital, are discussed in detail with particular reference to the common problems that might be observed. A second article in this two-part series, to be published in a subsequent issue of In Practice, will discuss second-line medical management of epilepsy.
OBJECTIVES: This study was designed to test the hypothesis that pain associated with syringomyelia in dogs is dependent upon size and involvement of the dorsal part of the spinal cord. METHODS: Masked observers determined syrinx dimensions and precise location within the spinal cord on magnetic resonance images of 55 cavalier King Charles spaniels with syringomyelia. After removal of masking, syrinx size and location were compared between the cohorts of dogs that exhibited pain with those that did not. RESULTS: Maximum syrinx width was the strongest predictor of pain, scratching behaviour and scoliosis in dogs with syringomyelia. Both pain and syrinx size were positively correlated with syrinxes located in the dorsal half of the spinal cord. CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE: Large syrinxes associated with damage to the dorsal part of the spinal cord are associated with persistent pain suggesting that the pain behaviour expressed by this group of patients is likely to be "neuropathic pain," resulting from disordered neural processing in the damaged dorsal horn. As such it is likely that conventional analgesic medication may be ineffective.
Canine Chiari-like malformation (CM) is a complex abnormality of the skull and craniocervical junction associated with miniaturization and brachycephaly which can result in the spinal cord disease syringomyelia (SM). This study investigated the inheritance of CM in a Griffon Bruxellois (GB) family and feasibility of crossbreeding a brachycephalic CM affected GB with a mesaticephalic normal Australian terrier and then backcrossing to produce individuals free of the malformation and regain GB breed characteristics. The study family cohort (n = 27) included five founder dogs from a previous baseline study of 155 GB which defined CM as a global malformation of the cranium and craniocervical junction with a shortened skull base and increased proximity of the cervical vertebrae to the skull. T1-weighted sagittal DICOM images of the brain and craniocervical junction were analysed for five significant traits (two angles, three lines) identified from the previous study and subsequent Qualitative Trait Loci analysis. Mean measurements for mixed breed, pure-breed and baseline study groups were compared. Results indicated that mixed breed traits posed less risk for CM and SM and were useful to distinguish the phenotype. Moreover on the MR images, the filial relationships displayed by the traits exhibited segregation and those presenting the greatest risk for CM appeared additive towards the severity of the condition. The external phenotypes revealed that by outcrossing breed types and with careful selection of appropriate conformation characteristics in the first generation, it is possible to regain the GB breed standard and reduce the degree of CM. The four GB affected with SM in the study all exhibited reduced caudal skull development compared to their relatives. The craniocervical traits may be useful for quantifying CM and assessing the possibility of SM thus assisting breeders with mate selection. However, such a system requires validation to ensure appropriateness for all breeds at risk.
Many of the molecular and pathological features associated with human Alzheimer disease (AD) are mirrored in the naturally occurring age-associated neuropathology in the canine species. In aged dogs with declining learned behaviour and memory the severity of cognitive dysfunction parallels the progressive build up and location of Aβ in the brain. The main aim of this work was to study the biological behaviour of soluble oligomers isolated from an aged dog with cognitive dysfunction through investigating their interaction with a human cell line and synthetic Aβ peptides. We report that soluble oligomers were specifically detected in the dog’s blood and cerebrospinal fluid via anti-oligomer- and anti-Aβ specific binders. Importantly, our results reveal the potent neurotoxic effects of the dog’s cerebrospinal fluid on cell viability and the seeding efficiency of the cerebrospinal fluid-borne soluble oligomers on the thermodynamic activity and the aggregation kinetics of synthetic human Aβ. The value of further characterising the naturally occurring Alzheimer-like neuropathology in dogs using genetic and molecular tools is discussed.
Chiari-like malformation (CM) is a developmental abnormality of the craniocervical junction that is common in the Griffon Bruxellois (GB) breed with an estimated prevalence of 65%. This disease is characterized by overcrowding of the neural parenchyma at the craniocervical junction and disturbance of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow. The most common clinical sign is pain either as a direct consequence of CM or neuropathic pain as a consequence of secondary syringomyelia. The etiology of CM remains unknown but genetic factors play an important role. To investigate the genetic complexity of the disease, a quantitative trait locus (QTL) approach was adopted. A total of 14 quantitative skull and atlas measurements were taken and were tested for association to CM. Six traits were found to be associated to CM and were subjected to a whole-genome association study using the Illumina canine high density bead chip in 74 GB dogs (50 affected and 24 controls). Linear and mixed regression analyses identified associated single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) on 5 Canis Familiaris Autosomes (CFAs): CFA2, CFA9, CFA12, CFA14 and CFA24. A reconstructed haplotype of 0.53 Mb on CFA2 strongly associated to the height of the cranial fossa (diameter F) and an haplotype of 2.5 Mb on CFA14 associated to both the height of the rostral part of the caudal cranial fossa (AE) and the height of the brain (FG) were significantly associated to CM after 10 000 permutations strengthening their candidacy for this disease (P = 0.0421, P = 0.0094 respectively). The CFA2 QTL harbours the Sall-1 gene which is an excellent candidate since its orthologue in humans is mutated in Townes-Brocks syndrome which has previously been associated to Chiari malformation I. Our study demonstrates the implication of multiple traits in the etiology of CM and has successfully identified two new QTL associated to CM and a potential candidate gene.
Syringomyelia is a condition that results in fluid-containing cavities within the parenchyma of the spinal cord as a consequence of altered cerebrospinal fluid dynamics. This review discusses the history and the classification of the disorder, the current theories of pathogenesis, and the advanced imaging modalities used in the diagnosis. The intramedullary pulse pressure theory (a new pathophysiologic concept of syringomyelia) also is presented. In addition, the current understanding of the painful nature of this condition is discussed and the current trends in medical and surgical management are reviewed.
Syringomyelia (SM) is a spinal cord disease that can cause neuropathic pain in dogs. The pathogenesis of SM secondary to Chiari-like malformation (CM) has been the focus of intense research in recent years. The gulf in our understanding of CM/SM in dogs relative to the analogous human condition has progressively narrowed. CM is primarily a disease of abnormal geometric morphometry affecting the caudal cranial fossa and the brain parenchyma contained within it. This review describes how advanced imaging techniques have revealed a series of morphometric abnormalities associated with CM/SM. The series is presented in a logical order to help describe the pathogenesis of CM and the subsequent formation of syringes, with particular reference to the concepts of craniospinal compliance and cerebrospinal fluid pulse pressure timing.
Background: Syringomyelia (SM) is a common condition affecting brachycephalic toy breed dogs and is characterized by the development of fluid-filled cavities within the spinal cord. It is often concurrent with a complex developmental malformation of the skull and craniocervical vertebrae called Chiari-like malformation (CM) characterized by a conformational change and overcrowding of the brain and cervical spinal cord particularly at the craniocervical junction. CM and SM have a polygenic mode of inheritance with variable penetrance. Results: We identified six cranial T1-weighted sagittal MRI measurements that were associated to maximum transverse diameter of the syrinx cavity. Increased syrinx transverse diameter has been correlated previously with increased likelihood of behavioral signs of pain. We next conducted a whole genome association study of these traits in 65 Cavalier King Charles Spaniel (CKCS) dogs (33 controls, 32 with extreme phenotypes). Two loci on CFA22 and CFA26 were found to be significantly associated to two traits associated with a reduced volume and altered orientation of the caudal cranial fossa. Their reconstructed haplotypes defined two associated regions that harbor only two genes: PCDH17 on CFA22 and ZWINT on CFA26. PCDH17 codes for a cell adhesion molecule expressed specifically in the brain and spinal cord. ZWINT plays a role in chromosome segregation and its expression is increased with the onset of neuropathic pain. Targeted genomic sequencing of these regions identified respectively 37 and 339 SNPs with significantly associated P values. Genotyping of tagSNPs selected from these 2 candidate loci in an extended cohort of 461 CKCS (187 unaffected, 274 SM affected) identified 2 SNPs on CFA22 that were significantly associated to SM strengthening the candidacy of this locus in SM development. Conclusions: We identified 2 loci on CFA22 and CFA26 that contained only 2 genes, PCDH17 and ZWINT, significantly associated to two traits associated with syrinx transverse diameter. The locus on CFA22 was significantly associated to SM secondary to CM in the CKCS dog breed strengthening its candidacy for this disease. This study will provide an entry point for identification of the genetic factors predisposing to this condition and its underlying pathogenic mechanisms.
Over the last 15 years, research on canid cognition has revealed that domestic dogs possess a surprising array of complex socio‐cognitive skills pointing to the possibility that the domestication process might have uniquely altered their brains; however, we know very little about how evolutionary processes (natural or artificial) might have modified underlying neural structure to support species‐specific behaviors. Evaluating the degree of cortical folding (i.e., gyrification) within canids may prove useful, as this parameter is linked to functional variation of the cerebral cortex. Using quantitative magnetic resonance imaging to investigate the impact of domestication on the canine cortical surface, we compared the gyrification index (GI) in 19 carnivore species, including six wild canid and 13 domestic dog individuals. We also explored correlations between global and local GI with brain mass, cortical thickness, white and grey matter volume and surface area. Our results indicated that GI values for domestic dogs are largely consistent with what would be expected for a canid of their given brain mass, although more variable than that observed in wild canids. We also found that GI in canids is positively correlated with cortical surface area, cortical thickness and total cortical grey matter volumes. While we found no evidence of global differences in GI between domestic and wild canids, certain regional differences in gyrification were observed.
The characteristics of magnetic resonance imaging (mri) of the brains and spinal cords of 11 dogs with histologically confirmed granulomatous meningoencephalomyelitis (gme) were determined. The lesions were in the brain of eight of the dogs, in the brain and spinal cord of two, and in the spinal cord alone in one dog. A single lesion was present in four of the dogs and multiple lesions were found in six. In one dog with intracranial signs, no visible lesions could be detected on mri. No meningeal enhancement was detected in T1-weighted images post-contrast, or in fluid attenuation inversion recovery (flair) images, but there were histological lesions in the meninges in nine of the dogs. The T2-weighted images and flair sequences were characterised in all cases by hyperintensity, whereas the signal intensity of the lesions on T1-weighted images was variable. After the administration of paramagnetic contrast, some of the lesions showed no enhancement, but others showed marked patterns of enhancement. The lesions in 10 of the dogs were easily identifiable by mri and the images had several unifying characteristics, but they could not be considered disease-specific.
A portosystemic shunt is an abnormal communication between the portal vascular system and the systemic circulation. A significant number of clinical signs associated with portosystemic shunting result from hepatic encephalopathy (HE); a syndrome encompassing neurological signs such as including changes in behaviour, ataxia, unresponsiveness, pacing, circling, blindness, seizures, coma and death. We present two West Highland White Terrier dogs diagnosed with HE based on clinical signs, bile acid stimulation test and imaging of the abnormal vessel communicating the portal and the systemic circulation. Magnetic resonance sequences of the brain revealed a poorly marginated and diffuse, bilateral and symmetric hyperintense lesions on T2-weighted, fluid attenuation inversion recovery and diffusion-weighted sequences relative to the brain parenchyma including the medial longitudinal fasciculus and reticular formation in the brainstem. No abnormalities were detected on T1-weighted sequences.
Chiari-like malformation (CM) and syringomyelia (SM) is a frequent diagnosis in predisposed brachycephalic toy breeds since increased availability of MRI. However, the relevance of that MRI diagnosis has been questioned as CM, defined as identification of a cerebellar herniation, is ubiquitous in some breeds and SM can be asymptomatic. This article reviews the current knowledge of neuroanatomical changes in symptomatic CM and SM and diagnostic imaging modalities used for the clinical diagnosis of CM-pain or myelopathy related to SM. Although often compared to Chiari type I malformation in humans, canine CM-pain and SM is more comparable to complex craniosynostosis syndromes (i.e., premature fusion of multiple skull sutures) characterized by a short skull (cranial) base, rostrotentorial crowding with rostral forebrain flattening, small, and ventrally orientated olfactory bulbs, displacement of the neural tissue to give increased height of the cranium and further reduction of the functional caudotentorial space with hindbrain herniation. MRI may further reveal changes suggesting raised intracranial pressure such as loss of sulci definition in conjunction with ventriculomegaly. In addition to these brachycephalic changes, dogs with SM are more likely to have craniocervical junction abnormalities including rostral displacement of the axis and atlas with increased odontoid angulation causing craniospinal junction deformation and medulla oblongata elevation. Symptomatic SM is diagnosed on the basis of signs of myelopathy and presence of a large syrinx that is consistent with the neuro-localization. The imaging protocol should establish the longitudinal and transverse extent of the spinal cord involvement by the syrinx. Phantom scratching and cervicotorticollis are associated with large mid-cervical syringes that extend to the superficial dorsal horn. If the cause of CSF channel disruption and syringomyelia is not revealed by anatomical MRI then other imaging modalities may be appropriate with radiography or CT for any associated vertebral abnormalities.
A hereditary, non-inflammatory myopathy occurring in young great Danes with distinctive histological features in muscle biopsy specimens is reviewed. Onset of clinical signs is usually before one year of age and both sexes are affected. Clinical signs are characterised by exercise intolerance, muscle wasting, and an exercise-induced tremor. Although most affected dogs have a severe form of the disease, occasional dogs may have a less pronounced form and survive into adulthood with an acceptable quality of life. Litters containing affected puppies are born to clinically unaffected parents, and an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance is likely. All recorded cases have had fawn or brindle coat coloration. Elevated serum creatinine kinase concentrations and spontaneous electrical activity in skeletal muscles are frequently found. While originally reported (Targett and others 1994) as a central core myopathy in this breed, the histochemical characteristics of the distinct cytoarchitectural structures differ from those of the well-characterised central core myopathy in human beings. In fact, these structures differ from any known myopathy in human beings and likely represents a unique non-inflammatory myopathy affecting dogs. Until this myopathy is characterised further, the name inherited myopathy in great Danes is suggested.
Modern interpretation of head conformation in the Cavalier King Charles spaniel (CKCS) has favoured a smaller, more exaggerated, brachycephalic type than originally described in the 1929 breed standard. Recent research studies identified brachycephaly and reduced hind cranium as two conformational (dysmorphic) features that increase risk for symptomatic Chiari-like malformation and secondary syringomyelia (SM). A prospective pilot study investigated the hypothesis that dysmorphic head features could be assessed visually and correlated with risk of SM. Thirteen CKCS, selected from anonymised photographic evidence, were physically appraised by authorised Kennel Club judges using a head shape checklist. These subjective evaluations were then matched with objective measurements of the cranium (cephalic index and rostrocaudal doming) and their subsequent MRI. A positive correlation (P=0.039) between the judges’ checklist score and rostrocaudal doming (hindskull ratio) and a positive correlation between the cephalic index and hindskull ratio (P=0.042) were identified. Five CKCS had no SM and their status tallied with 62 per cent of the judges’ evaluation. Although the ability of adjudicators to identify differences in head conformation varied, there was sufficient association between the dysmorphic parameters and the risk of SM to cause concern and propose a larger study in CKCS breed.
The number of cervical vertebrae in mammals is almost constant at seven, regardless of their neck length, implying that there is selection against variation in this number. Homebox (Hox) genes are involved in this evolutionary mammalian conservation, and homeotic transformation of cervical into thoracic vertebrae (cervical ribs) is a common phenotypic abnormality when Hox gene expression is altered. This relatively benign phenotypic change can be associated with fatal traits in humans. Mutations in genes upstream of Hox, inbreeding and stressors during organogenesis can also cause cervical ribs. The aim of this study was to describe the prevalence of cervical ribs in a large group of domestic dogs of different breeds, and explore a possible relation with other congenital vertebral malformations (CVMs) in the breed with the highest prevalence of cervical ribs. By phenotyping we hoped to give clues as to the underlying genetic causes. Twenty computed tomography studies from at least two breeds belonging to each of the nine groups recognized by the Federation Cynologique Internationale, including all the brachycephalic ‘screw‐tailed’ breeds that are known to be overrepresented for CVMs, were reviewed. The Pug dog was more affected by cervical ribs than any other breed (46%; P
Case series summary The aim of this case series was to describe the clinical presentation, imaging findings and histopathology of three cats with limited dorsal myeloschisis (LDM). The history, examination and MRI sequences were reviewed in three cases presented to a single referral hospital. The surgery report and histopathology were described in two cases. All cats were young (10 weeks old, 5 months old, 4 years old), presenting with varying degrees of progressive paraparesis. All had a midline skin defect overlying the spinal column that was either sunken or saccular, containing fluid thought to be cerebrospinal fluid. MRI sequences demonstrated tissue extending from the dura through an overlying bifid spinous process and attached to the dermis, with associated spinal cord tethering, atrophy and syringomyelia. Lesions were located at L2–L3, T8–T9 and L4. Histopathology described a fibroneural stalk with a glio-ependymal lining, surrounded by glial nests and nerve fibres. The youngest and most severely affected was euthanased, while the other two underwent surgery. Both regained independent ambulation with persistent paraparesis; however, one required ongoing management of urinary incontinence. Relevance and novel information LDM is a primary neural tube defect that may result in neurological deficits, including bladder dysfunction, and is characterised by a fibroneural stalk between the dermis and the spinal cord. Distinct MRI features, such as a visible intrathecal tract, dorsally tethered cord and syringomyelia, help distinguish this condition from the clinically similar dermoid sinus. The presence of progressive neurological signs, with a palpable midline defect overlying the affected spinal cord segment, may raise suspicion for this clinical entity in veterinary patients.
Two unrelated 8-month-old male mixed breed dogs were presented for evaluation of progressive ataxia, knuckling, and lack of pain perception in the distal limbs. Because of the similarity in age of onset, progression, and clinical findings with previously described sensory neuropathy in Border Collies, the affected dogs were screened for an FAM134B mutation and were determined to be homozygous for the mutation. Despite few phenotypic similarities with other breeds, genetic testing for specific diseases should be considered in mixed breed dogs with compatible clinical signs, especially if ancestry is unknown.
Two unrelated 8-month-old male mixed breed dogs were presented for evaluation of progressive ataxia, knuckling, and lack of pain perception in the distal limbs. Because of the similarity in age of onset, progression, and clinical findings with previously described sensory neuropathy in Border Collies, the affected dogs were screened for an FAM134B mutation and were determined to be homozygous for the mutation. Despite few phenotypic similarities with other breeds, genetic testing for specific diseases should be considered in mixed breed dogs with compatible clinical signs, especially if ancestry is unknown.
Background: Metronidazole is an antibacterial, antiprotozoal and anthelmintic medication commonly used in veterinary medicine. We describe cases of neurotoxicity associated with the drug’s administration. Methods: Medical records between 2004 and 2017 from four veterinary referral hospitals were reviewed. Inclusion criteria were the presence of neurological signs compatible with metronidazole toxicity, clinical history supporting recent metronidazole therapy and resolution of clinical signs upon discontinuation of metronidazole administration. Results: A total of 26 dogs were identified with clinical signs supporting a diagnosis of metronidazole toxicity. Median age at presentation was 7.2 years (range, 0.1–12 years); median duration of treatment was 35 days (range, 5–180 days); median treatment dosage was 21 mg/kg BID (range, 13–56 mg/kg every 12 h); median resolution of the clinical signs upon discontinuation of metronidazole was 3 days (range, 1–26 days). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain was performed in 19 cases and only one dog had brain lesions affecting the dentate nuclei, which resembled the MRI appearance of this disease in humans. Conclusions: We found evidence of neurotoxicity in dogs at much lower doses than previously reported and we suggest caution when administering metronidazole at doses > 40 mg/kg every 24 h, regardless of the duration of the treatment.
Objectives To characterise the symptomatic phenotype of Chiari-like malformation (CM), secondary syringomyelia (SM) and brachycephaly in the Cavalier King Charles Spaniel using morphometric measurements on mid-sagittal Magnetic Resonance images (MRI) of the brain and craniocervical junction. Methods This retrospective study, based on a previous quantitative analysis in the Griffon Bruxellois (GB), used 24 measurements taken on 130 T1-weighted MRI of hindbrain and cervical region. Associated brachycephaly was estimated using 26 measurements, including rostral forebrain flattening and olfactory lobe rotation, on 72 T2-weighted MRI of the whole brain. Both study cohorts were divided into three groups; Control, CM pain and SM and their morphometries compared with each other. Results Fourteen significant traits were identified in the hindbrain study and nine traits in the whole brain study, six of which were similar to the GB and suggest a common aetiology. The Control cohort had the most elliptical brain (p = 0.010), least olfactory bulb rotation (p = 0.003) and a protective angle (p = 0.004) compared to the other groups. The CM pain cohort had the greatest rostral forebrain flattening (p = 0.007), shortest basioccipital (p = 0.019), but a greater distance between the atlas and basioccipital (p = 0.002) which was protective for SM. The SM cohort had two conformation anomalies depending on the severity of craniocervical junction incongruities; i) the proximity of the dens (p
Syringomyelia is a condition characterised by fluid filled cavities (syrinxes or syringes) within the central spinal cord and the resulting damage produces clinical signs of pain and neurological deficits. Since the increase in availability of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), syringomyelia is an increasingly common diagnosis in veterinary medicine [1, 2] The most common cause of syringomyelia in the dog is Chiari-like malformation (Fig 1), a condition analogous to Chiari Type I and 0 malformation in humans [3, 4].
The pain behaviour expressed by dogs with syringomyelia suggests that they experience neuropathic pain, probably due to disordered neural processing in the damaged dorsal horn. As such it is likely that conventional analgesic medication will be ineffective. In this review, physiological and pathological pain processing through the dorsal horn is summarised and mechanisms by which syringomyelia could result in a persistent pain state are discussed. Finally, current knowledge regarding treatment of Chiari malformation and syringomyelia is reviewed and possible drugs which may give improved pain relief in affected dogs are discussed.
Canine Lafora disease is a recessively inherited, rapidly progressing neurodegenerative disease caused by the accumulation of abnormally constructed insoluble glycogen Lafora bodies in the brain and other tissues due to the loss of NHL repeat containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 (NHLRC1). Dogs have a dodecamer repeat sequence within the NHLRC1 gene, which is prone to unstable (dynamic) expansion and loss of function. Progressive signs of Lafora disease include hypnic jerks, reflex and spontaneous myoclonus, seizures, vision loss, ataxia and decreased cognitive function. We studied five dogs (one Chihuahua, two French Bulldogs, one Griffon Bruxellois, one mixed breed) with clinical signs associated with canine Lafora disease. Identification of polyglucosan bodies (Lafora bodies) in myocytes supported diagnosis in the French Bulldogs; muscle areas close to the myotendinous junction and the myofascial union segment had the highest yield of inclusions. Postmortem examination of one of the French Bulldogs revealed brain Lafora bodies. Genetic testing for the known canine NHLRC1 mutation confirmed the presence of a homozygous mutation associated with canine Lafora disease. Our results show that Lafora disease extends beyond previous known breeds to the French Bulldog, Griffon Bruxellois and even mixed-breed dogs, emphasizing the likely species-wide nature of this genetic problem. It also establishes these breeds as animal models for the devastating human disease. Genetic testing should be used when designing breeding strategies to determine the frequency of the NHLRC1 mutation in affected breeds. Lafora diseases should be suspected in any older dog presenting with myoclonus, hypnic jerks or photoconvulsions.
Objectives There is a paucity of information on feline discospondylitis. This study aimed to describe the signalment, clinical and laboratory findings, aetiological agents, treatment and outcome in cats affected by discospondylitis. Methods This was a retrospective review of the medical records of cats diagnosed with discospondylitis at four referral institutions. Results A total of 17 cats were identified. Most were domestic shorthair cats (76.5%) and male (58.8%), with a median age of 9 years (range 0.9–14) and a median duration of clinical signs of 3 weeks (range 0.3–16). All cats presented with spinal hyperaesthesia; 3/17 had pyrexia. Neurological dysfunction was found in 64.7% of cats, which was indicative of a T3–L3 or L4–S2 spinal segment, associated nerve root or associated nerve neurolocalisation. Haematology, serum biochemistry and urinalysis revealed occasional inconsistent non-specific changes. All cats underwent urine culture; 9/17 cats also had a distinct tissue cultured. Positive bacterial cultures were obtained in two cats (11.8%) for Staphylococcus species (urine, blood and intradiscal fine-needle aspirate) and Escherichia coli (urine); both presented with multifocal discospondylitis. Treatment was non-surgical in all cats, with sustained antibiotic therapy for a median of 3 months (range 1–9). Analgesia provided included non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, alone or in combination with gabapentin. Restricted exercise was advised for a minimum of 4 weeks. Outcome information available in 12 cats was excellent in terms of pain control and neurological function in 10 cats (83.3%) at the time of stopping antibiotics. Recurrence occurred in one case, which had received a single antibiotic for 6 weeks, and relapsed 4 months after presentation. One other case failed to improve and was euthanased during the course of hospitalisation. Conclusions and relevance Feline discospondylitis is uncommon and no obvious signalment predisposition was found in this study. Spinal hyperaesthesia was universally present, with neurological dysfunction also highly prevalent. Bacterial culture was unrewarding in most cases. Amoxicillin–clavulanic acid or cephalosporins are reasonable choices for first-line antibiotics. Prognosis was favourable, with no long-term evidence of recurrence in cats on sustained antibiotic therapy, for a mean duration of 3 months.
Additional publications
Books and Book chapters
Graham Flint (Editor) Clare Rusbridge (Editor). (2014). Syringomyelia: A Disorder of CSF Circulation: Current Understanding, Best Clinical Practice and Research Perspectives. Springer
Book Chapters
- Neck and back pain – BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Neurology
- Tremors. Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine – 2021 9th 2016 8th Edition. Elsevier
- Brain disorders associated with brachycephaly in Health and Welfare of Brachycephalic (Flat-faced) Companion Animals A Complete Guide for Veterinary and Animal Professionals ISBN 9780367207243
- Feline Orofacial Pain. Feline Behavioral Health and Welfare. 2015 Elsevier (First Listed author, co-author with Sarah Heath)
- Syringomyelia and Chiari malformation. 5 Minute Veterinary Consult Canine and Feline: 7th (2020), 6th (2015), 5th (2011), 4th (2007) Editions Blackwell Publishing
- Treatment of Chiari malformation and Syringomyelia. Kirk’s Current Veterinary Therapy XIV 2015. Saunders Elsevier
- Nomenclature. Syringomyelia: A Disorder of CSF Circulation.2014 Springer (First Listed author, co-author with Graham Flint)
- Veterinary Aspects. Syringomyelia: Springer A Disorder of CSF Circulation.2014 Springer
- Historical Vingnettes. Syringomyelia: A Disorder of CSF Circulation. 2014 Springer (Second Listed author, co-author with Graham Flint)
- Pain Management. Syringomyelia: A Disorder of CSF . 2014 Springer (Second Listed author, co-author with Jan Keppel Hesselink)
- Treatment of Chiari malformation and Syringomyelia in Kirk’s Current Veterinary Therapy XIV edBonagura, J.D. and Twedt D.C. Saunders Elsevier Missouri 2009 Chapter 240 pp1102-1107
- Neurological Infections. In: BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Infectious Diseases ed Ramsey I and Tennant B BSAVA 2001 pp231- 249