A manifesto for change: Prioritise nurses, midwives and paramedics' psychological health to strengthen the NHS culture
A focus on the psychological wellbeing of nurses, midwives, and paramedics is an important catalyst to revitalise the NHS, say researchers at the University of Surrey. The team are launching a guide targeted at helping the three professions thrive at work and deliver high-quality care to patients, often in challenging and emotionally taxing circumstances.
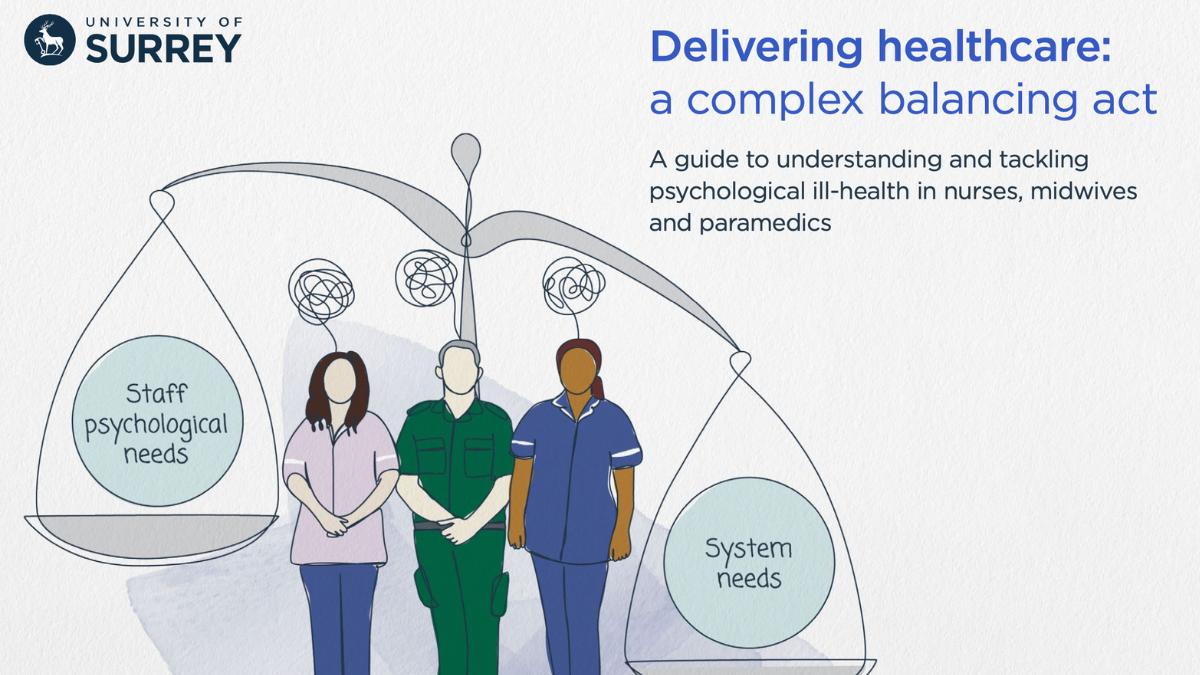
The guide, entitled 'Delivering Healthcare: A Complex Balancing Act - a Guide to Understanding and Tackling Psychological Ill-health in Nurses, Midwives and Paramedics' is the result of a comprehensive National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) funded study conducted in 2020-2022 to understand why psychological ill-health persists despite interventions to prevent it.
Recommendations from the guide
The guide makes six recommendations targeted at Wellbeing Guardians (leaders looking to improve staff wellbeing at work and NHS culture), executive boards, senior leaders, team managers and anyone working to improve the psychological health of nurses, midwives and paramedics. The recommendations are:
Prioritise essential needs
Make sure the basic needs of staff, like access to food, rest areas, and appropriate work resources, are met. This forms the foundation for effective work.
Take a systems approach to staff support and share good practice
Ensure psychological health is not the responsibility of individuals alone - it is a collective endeavour. Review and develop support systems, sharing good practices and addressing gaps in staff support. Extend support programmes, such as the Practitioner Health Programme, beyond doctors and dentists. Ensure Wellbeing Guardians have sufficient resources.
Normalise and anticipate psychological health management
Acknowledge that stress and burnout are inevitable in healthcare. Implement strategies for early discussions about psychological health (including with students) and develop long-term plans to manage and mitigate these risks.
Give equal emphasis to psychological and physical harm
Focus on psychological health needs and preventing harm, not only the risk of physical injury. Run risk assessments for psychological wellbeing similar to those for physical safety.
Nurture compassionate leaders
Invest in future leaders with a focus on compassionate, inclusive leadership. Provide support and training for new leaders and integrate leadership skills development from the beginning by integrating them into courses for students joining the professions.
Foster learning over blame culture
Encourage a culture where staff can speak up about issues without fear of blame or punishment. Develop and change the organisational culture to support psychological safety and collective accountability and address unprofessional behaviours.
Key findings
The recommendations from the guide address five key findings/ tensions from the team's research:
Blame culture impedes staff wellness
A blame culture focusing on individual errors conflicts with a team-based approach, hindering staff psychological wellness by discouraging open communication.
'Serve and sacrifice' can impede staff wellbeing
Healthcare's 'serve and sacrifice' ethos, prioritising institutional needs, leads to staff overwork and moral distress, especially amid staff shortages.
The costs of upholding values
Discrepancies between healthcare's ideal values and practical realities cause staff emotional distress. Required empathy in patient care risks vicarious trauma, highlighting the need for better management of emotional labour.
Fragmented interventions and chronic stress
Current interventions, often individual-focused and fragmented, fail to comprehensively address systemic issues and chronic stressors in healthcare.
The challenges in designing interventions to work optimally with diverse staff
Designing effective, diverse staff interventions is complex. The balance between mandatory and voluntary programmes and the timing and nature of interventions often limit their effectiveness.
Download and read the guide from the research team's website.
Disclaimer: This project was supported by the NIHR HS&DR programme with grant number 129528. The views and opinions expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the HS&DR programme.
Notes to editors
The mission of the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) is to improve the health and wealth of the nation through research by:
- Funding high-quality, timely research that benefits the NHS, public health and social care.
- Investing in world-class expertise, facilities and a skilled delivery workforce to translate discoveries into improved treatments and services.
- Partnering with patients, service users, carers and communities to improve the relevance, quality and impact of our research.
- Attracting, training and supporting the best researchers to tackle complex health and social care challenges.
- Collaborating with other public funders, charities and industry to help shape a cohesive and globally competitive research system.
- Funding applied to global health research and training to meet the needs of the poorest people in low and middle-income countries.
NIHR is funded by the Department of Health and Social Care. Its work in low and middle-income countries is principally funded through UK Aid from the UK government.
Featured Academics
Media Contacts
External Communications and PR team
Phone: +44 (0)1483 684380 / 688914 / 684378
Email: mediarelations@surrey.ac.uk
Out of hours: +44 (0)7773 479911

